Naringin mitigated doxorubicin-induced kidney injury by the reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation with a synergistic anticancer effect
- PMID: 40551188
- PMCID: PMC12186448
- DOI: 10.1186/s40360-025-00947-7
Naringin mitigated doxorubicin-induced kidney injury by the reduction of oxidative stress and inflammation with a synergistic anticancer effect
Abstract
Background: The pathophysiology and severity of kidney impairment due to doxorubicin (DOX) treatment are markedly influenced by oxidative stress and inflammation. Naringin (NG), a natural flavonoid, has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. The nephroprotective effect of NG on DOX-induced kidney toxicity was investigated to increase its utility in clinical settings.
Methods: DOX toxicity was induced by a single ip injection (15 mg/kg) and for possible protection NG (100 mg/Kg) was used.
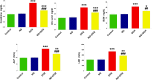
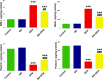
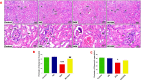
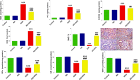
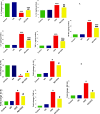
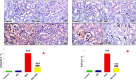
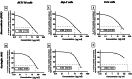
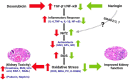
Results: Kidney damage and dysfunction were indicated by an elevation in the levels of creatinine, urea, uric acid, and the activity of ALP and LDH in serum, KIM-1, and NAGAL in kidney, and a significant decrease in nephrin and podocin in renal tissue. These disrupted glomerular and tubular function indicators were remarkably ameliorated by oral administration of NG (100 mg/kg) daily for 10 days before DOX treatment and continued for an additional four days post-Dox treatment. The nephroprotective effect of NG was confirmed by the improvement of histopathological and PAS histochemical investigations. The mitigating impact of NG was verified by normalization of the redox balance, evidenced by a significant amelioration of ROS levels, oxidative stress markers (MDA, PC, 8-OHdG), and antioxidants (GSH, GPx, GR), as well as upregulation of Nrf2 expression in kidney. Furthermore, NG significantly prevented the increase in the inflammatory mediators (IL-6, IL-1β, TNF-α, and NF-κB) and upregulated the anti-inflammatory IL-10 in DOX-treated rats. The expression of TGF-β1 and the apoptotic protein caspase-3 in the kidneys significantly decreased as a result of the improvement in redox state in renal tissue. Additionally, NG demonstrated anticancer effects and their combination showed synergistic anticancer impact on larynx and colon cancer cell lines in vitro study.
Conclusions: NG demonstrated remarkable protection of kidney against DOX treatment.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Doxorubicin; Inflammation; Kidney histopathology; Kidney injury; Naringin.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Institutional animal care and use committee (ACUC) of Mansoura University approved the legislation used in this work, which complies with international standards for laboratory animal handling and care (approval number: MU-ACUC (SC. PhD. 23.09.13)). Consent for publication: Not applicable Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Aegeline improves doxorubicin-induced liver toxicity by modulating oxidative stress and Bax/Bcl2/caspase/NF-κB signaling.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 26;15(1):27203. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-09675-8. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40715307 Free PMC article.
-
Metformin alleviates doxorubicin-induced hepatic damage by modulating oxidative stress: a molecular, biochemical, and histopathological approach in a rat model.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):9099-9107. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03688-2. Epub 2025 Feb 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39903256
-
Effect of dapagliflozin on sepsis-induced kidney injury in a rat model: modulation of the NLRP3 pathway.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2025 Aug;47(4):533-540. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2025.2519597. Epub 2025 Jun 18. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2025. PMID: 40533406
-
The effect of immunomodulatory properties of naringenin on the inhibition of inflammation and oxidative stress in autoimmune disease models: a systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical evidence.Inflamm Res. 2022 Nov;71(10-11):1127-1142. doi: 10.1007/s00011-022-01599-7. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 35804246
-
Bisphosphonates for breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;(3):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012 Feb 15;(2):CD003474. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003474.pub3. PMID: 16034900 Updated.
Cited by
-
Doxorubicin Toxicity and Recent Approaches to Alleviating Its Adverse Effects with Focus on Oxidative Stress.Molecules. 2025 Aug 7;30(15):3311. doi: 10.3390/molecules30153311. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40807486 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ibrahim Fouad G, Ahmed KA. The protective impact of berberine against doxorubicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Tissue Cell. 2021;73:101612. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

