Diagnostic performance of plasma Aβ42/40 ratio, p-tau181, GFAP, and NfL along the continuum of Alzheimer's disease and non-AD dementias: An international multi-center study
- PMID: 40551285
- PMCID: PMC12185245
- DOI: 10.1002/alz.14573
Diagnostic performance of plasma Aβ42/40 ratio, p-tau181, GFAP, and NfL along the continuum of Alzheimer's disease and non-AD dementias: An international multi-center study
Abstract
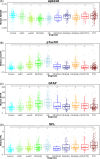
Introduction: Plasma phosphorylated tau (p-tau)181, glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP), neurofilament light chain (NfL), and amyloid beta ratio (Aβ42/40) may have diagnostic and prognostic value in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Here we assess which markers can best identify AD from controls and other non-AD dementias in a large international multi-center study.
Methods: Plasma samples (n = 1298) were collected from six international centers. Aβ40, Aβ42, GFAP, NfL, and p-tau181 were measured using single molecule array. In each group, AD diagnosis/co-pathology was defined according to cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers or amyloid positron emission tomography. Validations were performed in three separate cohorts via single and dual cut-off models.
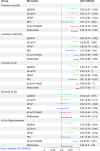
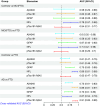
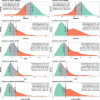
Results: p-tau181 showed the best area under the curve value to separate AD from frontotemporal dementia, controls, and Aβ- dementia with Lewy bodies. However, this discriminative power could not be reproduced by applying pre-defined cut-offs.
Discussion: p-tau181 was the best single plasma marker for detecting AD at any stage. Specific cut-offs are needed to maximize diagnostic performances.
Highlights: Phosphorylated tau (p-tau)181 provided a clear differentiation between controls and Alzheimer's disease (AD) participants, with evidence of increased levels in the preclinical stage of AD. Plasma biomarkers demonstrated that when amyloid co-pathology is removed from dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), only glial fibrillary acidic protein and neurofilament light chain remain to predict DLB. Given the low prevalence of amyloid co-pathology in frontotemporal dementia (FTD), p-tau181 and its ratio with amyloid beta 42 are strong biomarkers to differentiate FTD from AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; amyloid beta; dementia with Lewy bodies; frontotemporal dementia; plasma biomarkers.
© 2025 The Author(s). Alzheimer's & Dementia published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of Alzheimer's Association.
Conflict of interest statement
J.D., E.J.M., P.O.R., A.F.L., J.C., A.G.E., C.M., Y.P., A.T., M.K.S., I.H., L.B., C.F., K.V., S.I.V., and S.H. have no conflicts of interest to declare. G.B. has grants or contracts from the Parkinson's Foundation, Fujirebio, and the Alzheimer's Association. L.V. has grants or contracts from NWO VENI and Amsterdam UMC, ZonMw, Olink Dioraphte, Roche Diagnostics, Ely Lilly, Alzheimer's Association, Alzheimer Nederland, and Dutch Dementia researchers conference committee. D.A. has support from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, and the Department of Health Generalitat de Catalunya PERIS program, and funding from Grfols S.A., Lily, Fujirebio, Roche Diagnostics, Nutricia, Krka Farmaceutical SL, Zambon SAU, Esteve Pharmaceuticals, and Neuraxpharm. N.M.C. received support from the Swedish Alzheimer Foundation, Family Ronnstrom Foundation, Swedish Brain Foundation, Kock Foundation, WASP and DDLS joint call for research projects, Konug Gustaf V:s och Drottning Victorias Frimurarestiftelse, the Swedish Research Council, Biogen, and Owkin. I.V. has grants, funding, or contracts from the Amsterdam UMC starter grant, and the TKI grant Health‐Holland, Neurogen Biomarking, and Quanterix. L.G. has received grants or contracts from AirAlzh Foundation; received consulting fees from Fujirebio and Eli Lilly; has payment or honoraria from Fujirebio, Eli Lilly, and Eisai; and support for attending meetings and/or travel from Fujirebio, Eli Lilly, and Novartis. L.G. also participates on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for Eli Lilly. A.W. received support from Quanterix and a grant from the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation program under the Marie Skłodowska‐ Curie. J.F. received support from Fondo de Investigaciones Sanitario (FIS); Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain; National Institutes of Health (NIH), USA; Generalitat de Catalunya, Spain; Fundació Tatiana Pérez de Guzmán el Bueno, Spain; Alzheimer ´s Association, USA; Brightfocus, USA; and Horizon 2020 (European Commission). J.F. received consulting fees from Lundbeck, Ionis, and AC Immune, and payments or honoraria from Roche Diagnostics, Esteve, Biogen, Laboratorios Canot, MKI, Eisai, Lilly, and Adamed. J.F. has patent issued; WO2019175379 A1 Markers of synaptopathy in neurodegenerative disease. J.F. participates on a data safety monitoring board or advisory board for AC Immune, Alzheon, Zambon, Lilly, Roche Diagnostics, Eisai, and Perha. J.F. has leadership or fiduciary roles in the Spanish Neurological Society, T21 Research Society, Lumind Foundation, Jerome‐Lejeune Foundation, Alzheimer's Association, Health Research Board, Dementia Trials Ireland, European Commission, National Institutes of Health, USA, and the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Spain. J.F. has receipt of equipment, materials, drugs, medical writing, gifts. or other services from Life Molecular Imaging (LMI). M.O. received grants or contracts from the BMBF – FTLD consortium, moodmarker, the ALS association, and EU_MIRIADE, and funding from Biogen, Axon, Roche Diagnostics, and Grifols. M.O. participates on a data safety monitory or advisory board from the Biogen ATLAS trial, and has a leadership or fiduciary role in the German Society for CSF diagnostics and neurochemistry, as a speaker for the FTLD consortium, and for the Society for CSF diagnostics and neurochemistry. A.L. has grants or contracts from Hersenstichting and ZOnMW, and has a leadership or fiduciary role on the Steering Committee E‐DLB and the Dutch Neurology Society. W.F. has grants or contracts from ZonMW, NWO, EU‐FP7, EU‐JPND, Alzheimer Nederland, Hersenstichting CardioVascular Onderzoek Nederland, Health∼Holland, Topsector Life Sciences & Health, stichting Dioraphte, Gieskes‐Strijbis fonds, stichting Equilibrio, Noaber Foundation, Edwin Bouw fonds, Pasman stichting, Stichting Steun Alzheimercentrum Amsterdam, Philips, Biogen MA Inc, Novartis‐NL, Life‐MI, AVID, Roche BV, Fujifilm, Eisai, Combinostics. W.F. holds the Pasman chair. W.F. is recipient of ABOARD, which is a public–private partnership receiving funding from ZonMW (#73305095007) and Health∼Holland, Topsector Life Sciences & Health (PPP‐allowance; #LSHM20106). W.F. is recipient of TAP‐dementia, ZonMw #10510032120003. W.F. is recipient of IHI‐AD‐RIDDLE (#101132933), a project supported by the Innovative Health Initiative Joint Undertaking (IHI JU). W.F. is consultant to Oxford Health Policy, Forum CIC, Roche Diagnostics, Eisai, and Biogen MA Inc. W.F. has been an invited speaker at Boehringer Ingelheim, Biogen MA Inc, Danone, Eisai, WebMD Neurology (Medscape), NovoNordisk, Springer Healthcare, European Brain Council. W.F. participated on advisory boards of Biogen MA Inc, Roche Diagnostics, and Eli Lilly. WF is member of the steering committee of Novonordisk's Evoke/Evoke+ phase 3 trials. W.F. is member of the steering committee of PAVE, and Think Brain Health. W.F. was associate editor of
Figures

Similar articles
-
The impact of kidney function on Alzheimer's disease blood biomarkers: implications for predicting amyloid-β positivity.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Feb 19;17(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13195-025-01692-z. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39972340 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Plasma Amyloid, P-Tau, GFAP, and NfL With CSF, Clinical, and Cognitive Features in Patients With Dementia With Lewy Bodies.Neurology. 2024 Jun 25;102(12):e209418. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000209418. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Neurology. 2024. PMID: 38830138 Free PMC article.
-
Short-term variability of Alzheimer's disease plasma biomarkers in a mixed memory clinic cohort.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025 Jan 21;17(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s13195-024-01658-7. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 39838483 Free PMC article.
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer's disease in Down syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Alzheimers Dement. 2025 Apr;21(4):e70135. doi: 10.1002/alz.70135. Alzheimers Dement. 2025. PMID: 40219863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kließ MK, Martins R, Connolly MP. Major cost drivers in assessing the economic burden of Alzheimer's disease: a structured, rapid review. Jpad‐J Prevention of Alzheimers Dis. 2021;8(3):362‐370. - PubMed
-
- Boeve BF, Boxer AL, Kumfor F, Pijnenburg Y, Rohrer JD. Advances and controversies in frontotemporal dementia: diagnosis, biomarkers, and therapeutic considerations. Lancet Neurol. 2022;21(3):258‐272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- ADG-101096455/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- GHR Foundation
- 2022-00775/Swedish Research Council
- ERAPERMED2021-184/ERA PerMed
- 2022-0231/Knut and Alice Wallenberg foundation
- Strategic Research Area MultiPark
- Lund University
- AF-980907/Swedish Alzheimer Foundation
- FO2021-0293/Swedish Brain Foundation
- 1412/22/Parkinson foundation of Sweden
- Cure Alzheimer's fund
- Rönström Family Foundation
- Konung Gustaf V:s och Drottning Victorias Frimurarestiftelse
- 2020-O000028/Skåne University Hospital Foundation
- 2022-1259/Regionalt Forskningsstöd
- 2022-Projekt0080/Regionalt Forskningsstöd
- TriBEKa-17-519007/LCF/PR/GN17/50300004
- SGR 00913/LCF/PR/GN17/50300004
- European Commission
- Marie Curie International Training Network)
- Innovative Medicines Initiatives 3TR
- European Union's Horizon Europe Research
- Innovation Programme
- Alzheimer Association
- Health Holland
- NWO_/Dutch Research Council/Netherlands
- Alzheimer Drug Discovery Foundation
- The Selfridges Group Foundation
- Alzheimer Netherlands
- Dutch National Dementia Strategy
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

