An In Vitro Comparison of the Influence of Air Abrasion, G-Multiprimer, and Salivary Contamination on the Shear Bond Strength and Surface Characteristics of Opaque Zirconia Ceramics
- PMID: 40551785
- PMCID: PMC12185196
- DOI: 10.1155/ijod/3644666
An In Vitro Comparison of the Influence of Air Abrasion, G-Multiprimer, and Salivary Contamination on the Shear Bond Strength and Surface Characteristics of Opaque Zirconia Ceramics
Abstract
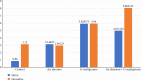
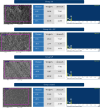
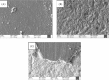
Aim: To evaluate the effect of various surface treatments and saliva contamination on the shear bond strength (SBS) and surface characteristics of yttria-stabilized tetragonal zirconia ceramics (YTZP) bonded with self-adhesive resin cement (SAC). Materials and Methods: Opaque Y-ZTP ceramics were divided into four groups based on specific surface treatment: control (C), air abrasion (AA), G-multiprimer (G), and AA + G (AG). Surface characteristics of the treated specimens, roughness and, elemental analysis were done using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), and energy dispersive analysis of X-rays (EDAX), respectively. These specimens were further divided into saliva (S) and non-S (NS) contamination groups. Following the surface treatment, 10 resin cement cylinders were affixed onto the zirconia discs within every group. Micro-SBS (µSBS) was calculated, and fracture surfaces were assessed. Statistical analysis was done using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and the post hoc Tukey test. Results: The µSBS values for the groups were as follows: CS (0.86 ± 0.7), CNS (3.13 ± 2.7), AS (3.14 ± 2.6), ANS (2.96 ± 1.2), GS (5.92 ± 2.2), GNS (5.94 ± 2.2), AGS (4.97 ± 0.9), and AGNS (8.06 ± 1.4). A one-way ANOVA showed that all the groups had a statistically significant difference in the SBS except the AS, AGS, CNS, ANS, as well as the GNS and AGNS. AFM results revealed the mean roughness value of AA is highest, followed by G-multiprimer, AG, and least in control. This difference is statistically significant with p-value of <0.001. This also correlated with the SEM images. Conclusion: Airborne particle abrasion and the application of G-multiprimer provide the best results in a moisture-free environment.
Keywords: G-multiprimer; air abrasion; resin cement; saliva contamination; zirconia.
Copyright © 2025 Alisha Ono Idris et al. International Journal of Dentistry published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Tan P. L., Gratton D. G., Diaz-Arnold A. M., Holmes D. C. An In Vitro Comparison of Vertical Marginal Gaps of CAD/CAM Titanium and Conventional Cast Restorations. Journal of Prosthodontics-Implant Esthetic and Reconstructive Dentistry . 2008;17(5):378–383. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-849X.2008.00302.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

