Radiofrequency Ablation as an Alternative and Novel Procedure in the Intraepithelial Neoplasia Management: A Systematic Scoping Review
- PMID: 40551867
- PMCID: PMC12183385
- DOI: 10.1002/hsr2.70938
Radiofrequency Ablation as an Alternative and Novel Procedure in the Intraepithelial Neoplasia Management: A Systematic Scoping Review
Abstract
Background and aims: Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) has emerged as a promising minimally invasive technique for eliminating intraepithelial neoplasia (IEN). We reviewed current evidence investigating the role of RFA in managing different types of IEN.
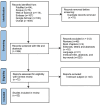
Methods: A systematic review was conducted to assess the current evidence for the use of RFA in managing various types of IEN. A three-step search strategy was employed, involving keyword extraction, comprehensive database searching (PubMed, Scopus, Web of Science, Embase, and Google Scholar), and reference screening.
Results: Thirty-two articles were included in this review, and most of the literature reported the features of RFA in the esophagus-related IENs (68.7%). RFA treatment was also found to effectively address gastric (9.3%), anal (12.5%), and cervical (9.3%) IENs. The general opinion on using RFA in Barrett's esophagus (BE) was its combination therapy with the endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) methods, which suggested better outcomes than RFA/EMR monotherapy. RFA was not preferred treatment for high-grade gastric dysplasia, but it was effective for the low-grade type.
Conclusion: As a minimally invasive, safe, and effective procedure, RFA holds promise for addressing lesions associated with BE, gastric, anal, and cervical IEN; However, the scope and gaps related to RFA therapy require to be explored precisely.
Keywords: Barrett's esophagus; carcinoma in situ; endoscopic mucosal resection; intraepithelial neoplasia; radiofrequency ablation.
© 2025 The Author(s). Health Science Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Surveillance of Barrett's oesophagus: exploring the uncertainty through systematic review, expert workshop and economic modelling.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Mar;10(8):1-142, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta10080. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16545207
-
Ablative and non-surgical therapies for early and very early hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2023 Dec;27(29):1-172. doi: 10.3310/GK5221. Health Technol Assess. 2023. PMID: 38149643 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety outcomes of multimodal endoscopic eradication therapy in Barrett's esophagus-related neoplasia: a systematic review and pooled analysis.Gastrointest Endosc. 2017 Mar;85(3):482-495.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2016.09.022. Epub 2016 Sep 23. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017. PMID: 27670227
-
Efficacy and Safety of Advanced Endoscopic Techniques in Early Barrett's Neoplasia: A Systematic Review and Pooled Analysis.Cureus. 2025 Jun 14;17(6):e86015. doi: 10.7759/cureus.86015. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40661999 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interventions for great saphenous vein incompetence.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Aug 11;8(8):CD005624. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005624.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34378180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- O'Shaughnessy J. A., Kelloff G. J., Gordon G. B., et al., “Treatment and Prevention of Intraepithelial Neoplasia: An Important Target for Accelerated New Agent Development,” Clinical Cancer Research: An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 8, no. 2 (2002): 314–346. - PubMed
-
- Goldstone R. N., Hasan S. R., Drury S., Darragh T. M., van Zante A., and Goldstone S. E., “A Trial of Radiofrequency Ablation for Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia,” International Journal of Colorectal Disease 32, no. 3 (2017): 357–365. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials