Recent Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Related Technical Challenges in MALDI MS and MALDI-MSI: A Mini Review
- PMID: 40551965
- PMCID: PMC12183430
- DOI: 10.5702/massspectrometry.A0175
Recent Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Related Technical Challenges in MALDI MS and MALDI-MSI: A Mini Review
Abstract
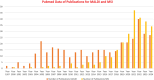
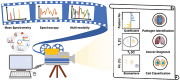
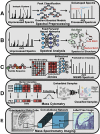
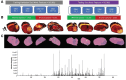
Artificial intelligence (AI) has provided viable methods for retrieving, organizing, and analyzing mass spectrometry (MS) data in various applications. However, several challenges remain as this technique is still in its early, preliminary stages. Critical limitations include the need for more effective methods for identification, quantification, and interpretation to ensure rapid and accurate results. Recently, high-throughput MS data have been leveraged to advance machine learning (ML) techniques, particularly in matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight (MALDI-TOF) MS and MS imaging (MSI). The accuracy of AI models is intricately linked to the sampling techniques used in MALDI and MALDI imaging measurements. With the help of artificial neural networks, traditional barriers are being overcome, accelerating data acquisition for different applications. AI-driven analysis of chemical specificity and spatial mapping in two-dimensional datasets has gained significant attention, highlighting its potential impact. This review focuses on recent AI applications, particularly supervised ML in MALDI-TOF MS and MALDI-MSI data analysis. Additionally, this review provides an overview of sample preparation methods and sampling techniques essential for ensuring high-quality data in deep learning-based models.
Keywords: MALDI; MS imaging; artificial intelligence; deep learning; machine learning.
© Author(s) 2025 Ali Farhan and Yi-Sheng Wang.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Systematic Review and Bibliometric Analysis of Applications of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Vascular Surgery.Ann Vasc Surg. 2022 Sep;85:395-405. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2022.03.019. Epub 2022 Mar 24. Ann Vasc Surg. 2022. PMID: 35339595
-
A deep learning approach to direct immunofluorescence pattern recognition in autoimmune bullous diseases.Br J Dermatol. 2024 Jul 16;191(2):261-266. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljae142. Br J Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38581445
-
Machine learning in knee arthroplasty: specific data are key-a systematic review.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022 Feb;30(2):376-388. doi: 10.1007/s00167-021-06848-6. Epub 2022 Jan 10. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2022. PMID: 35006281 Free PMC article.
-
The Use of AI for Phenotype-Genotype Mapping.Methods Mol Biol. 2025;2952:369-410. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-4690-8_21. Methods Mol Biol. 2025. PMID: 40553344
-
Performance of the matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry system for rapid identification of streptococci: a review.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017 Jun;36(6):1005-1012. doi: 10.1007/s10096-016-2879-2. Epub 2017 Jan 23. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28116553
References
-
- D. M. Camacho, K. M. Collins, R. K. Powers, J. C. Costello, J. J. Collins. Next-generation machine learning for biological networks. Cell 173: 1581–1592, 2018. - PubMed
-
- X. Chen, W. Shu, L. Zhao, J. Wan. Advanced mass spectrometric and spectroscopic methods coupled with machine learning for in vitro diagnosis. VIEW 4: 20220038, 2023.
-
- W. Jia, M. Sun, J. Lian, S. Hou. Feature dimensionality reduction: A review. Complex Intell. Syst. 8: 2663–2693, 2022.

