PKC in the perspective of dopamine receptor signaling
- PMID: 40552006
- PMCID: PMC12183092
- DOI: 10.3389/abp.2025.14488
PKC in the perspective of dopamine receptor signaling
Abstract
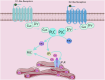
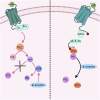
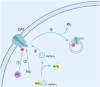
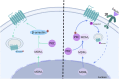
Protein kinase C (PKC) is widely distributed in various tissues, organs, and cells. By catalyzing the phosphorylation of Ser/Thr residues on various proteins, PKC regulates the metabolism, growth, proliferation, and differentiation of multiple cells and plays a crucial role in transmembrane signal transmission. In dopamine receptor signal transduction, PKC regulates numerous physiological functions, such as dopamine release, internalization of the dopamine transporter, downregulation of dopamine receptors, etc. In disease conditions, hyperactivation of PKC can lead to disorders such as schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease, while reduced PKC signaling may be associated with Alzheimer's disease. In the past few decades, researchers have paid increasing attention to the transduction role of PKC in dopamine receptor signaling, aiming to identify and discover potential targets for dopaminergic diseases. This review, from the perspective of signal transduction between dopamine receptors and PKC, reveals the pivotal hub position of PKC in the intracellular signal transduction network and its regulation of various physiological functions, providing ideas for future research on PKC and therapeutic interventions for dopaminergic diseases.
Keywords: dopamine receptor; dopaminergic disorders; physiological function; protein kinase C; signal transduction.
Copyright © 2025 Ma.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Association of Stimulant Use With Dopaminergic Alterations in Users of Cocaine, Amphetamine, or Methamphetamine: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.JAMA Psychiatry. 2017 May 1;74(5):511-519. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2017.0135. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28297025 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Ropinirole for levodopa-induced complications in Parkinson's disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;(1):CD001516. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001516. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. PMID: 11279718
-
The Long-Term Impact of Levodopa/Carbidopa Intestinal Gel on 'Off'-time in Patients with Advanced Parkinson's Disease: A Systematic Review.Adv Ther. 2021 Jun;38(6):2854-2890. doi: 10.1007/s12325-021-01747-1. Epub 2021 May 20. Adv Ther. 2021. PMID: 34018146 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of nicergoline in dementia and other age associated forms of cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001;2001(4):CD003159. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003159. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2001. PMID: 11687175 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

