Effect of smoking cessation on new-onset diabetes mellitus in dyslipidemic individuals: A population-based cohort study
- PMID: 40552061
- PMCID: PMC12184095
- DOI: 10.18332/tid/205418
Effect of smoking cessation on new-onset diabetes mellitus in dyslipidemic individuals: A population-based cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Smoking is a modifiable risk factor for diabetes mellitus, but the association between changes in smoking behavior and new-onset diabetes mellitus (NODM) in dyslipidemic patients remains unclear. This study aimed to examine how changes in smoking habits affect NODM risk among individuals with dyslipidemia.
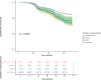
Methods: This retrospective cohort study used data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort (NHIS-NSC). A total of 34282 patients diagnosed with dyslipidemia between 2012 and 2014 were followed until December 2019 (median follow-up: 5 years). Smoking behavior change was defined by transitions in smoking status and intensity across two health examinations. NODM was identified by fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dL or ICD-10 codes E11-E14 with antidiabetic medication.
Results: During follow-up, 2479 participants (7.23%) developed NODM. Those with NODM had higher prevalence of obesity, abdominal obesity, hypertension, abnormal liver function, and family history of diabetes. Current smokers had increased NODM risk (hazard ratio, HR=1.36; 95% CI: 1.22-1.50) versus non-smokers. Heavy smokers had higher risk (HR=1.43; 95% CI: 1.24-1.60) than moderate smokers (HR=1.35; 95% CI: 1.16-1.60). Compared to continuous smokers, quitters had reduced risk (HR=0.79; 95% CI: 0.64-0.98), while reducers showed no significant risk reduction (HR=0.82; 95% CI: 0.63-1.08).
Conclusions: Among patients with dyslipidemia, smoking cessation was associated with a lower risk of NODM compared to continued smoking. These results suggest potential benefits of quitting smoking in reducing diabetes risk in this population.
Keywords: dyslipidemia; new-onset diabetes mellitus; retrospective cohort study; smoking behavior change.
© 2025 Seo W. et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have each completed and submitted an ICMJE form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. The authors declare that they have no competing interests, financial or otherwise, related to the current work. Ki. Lee reports that since the initial planning of the work, this study received support from the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund.
Figures
References
-
- International Diabetes Federation . IDF Diabetes Atlas. 10th edition; 2021. Accessed May 22, 2025. https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/previous-editions/
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources