Comparative effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib vs. adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 40552144
- PMCID: PMC12183229
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1524214
Comparative effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib vs. adalimumab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To provide the latest systematic review and meta-analysis comparing the effectiveness and safety of tofacitinib and adalimumab in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients.
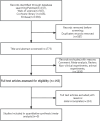
Methods: A systematic search of PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane databases was conducted until April 2025. Randomized controlled trials and cohorts comparing tofacitinib and adalimumab in RA patients were included. Outcomes assessed were significant improvements in American College of Rheumatology (ACR) 20 improvement criteria, changes in visual analog scale (VAS) (global activity), disease activity score (DAS) 28-C-reactive protein (CRP), Health Assessment Questionnaire-Disability Index (HAQ-DI), and adverse events. Sensitivity analyses and subgroup analysis evaluated the robustness of results and heterogeneity. Data analysis was performed using Review Manager 5.4.1 and STATA 15.0.
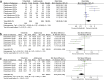
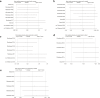
Results: Nine studies with 24,643 patients were analyzed. Tofacitinib showed superior effectiveness over adalimumab in ACR20 (risk ratio (RR): 1.28; 95% CI: 1.06, 1.55; P = 0.01), HAQ-DI (standardized mean difference (SMD): 0.20; 95% CI: 0.35, -0.05; P = 0.008), and VAS (SMD: 0.30; 95% CI: 0.56, -0.03; P = 0.03). No significant differences were found in adverse events (RR: 0.96; 95% CI: 0.89, 1.03; P = 0.22) or DSA28-CRP improvement (SMD: 0.02; 95% CI: 0.45, 0.02; P = 0.07). Sensitivity analyses confirmed stable outcomes for adverse events, HAQ-DI, and ACR20, but instability for VAS and DSA28-CRP. Subgroup analysis found that tofacitinib >5 mg twice daily was superior to ≤5 mg in terms of ACR20.
Conclusion: Tofacitinib was more effective than adalimumab in improving ACR20, VAS, and HAQ-DI, with no significant differences in adverse events or DSA28-CRP improvement.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/.
Keywords: adalimumab; meta-analysis; rheumatoid arthritis; systematic review; tofacitinib.
Copyright © 2025 Zhu, Zheng, Wang, Chen and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis unsuccessfully treated with biologics: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 10;3(3):CD012591. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012591. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28282491 Free PMC article.
-
Biologics or tofacitinib for people with rheumatoid arthritis naive to methotrexate: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 8;5(5):CD012657. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012657. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28481462 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Dec 22;12(12):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 9;1:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub3. PMID: 29271481 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
A systematic review of the effectiveness of adalimumab, etanercept and infliximab for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and an economic evaluation of their cost-effectiveness.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Nov;10(42):iii-iv, xi-xiii, 1-229. doi: 10.3310/hta10420. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 17049139
References
-
- Baker M. C., Liu Y., Lu R., Lin J., Melehani J., Robinson W. H. (2023). Incidence of interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biologic and targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs. JAMA Netw. open 6 (3), e233640. 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.3640 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bergman M., Chen N., Thielen R., Zueger P. (2022). One-year medication adherence and persistence in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in clinical practice: retrospective analysis of upadacitinib, adalimumab, baricitinib, and tofacitinib. J. Manag. Care Specialty Pharm. 28 (10), S102–S103. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

