Targeting the gut microbiota and lipid metabolism: potential mechanisms of natural products for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 40552158
- PMCID: PMC12183287
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1610498
Targeting the gut microbiota and lipid metabolism: potential mechanisms of natural products for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
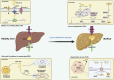
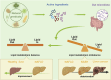
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a chronic progressive liver disease with overnutrition and insulin resistance (IR) as the main etiologic factors. Hepatic lipid accumulation is a central factor contributing to this cascade of changes. Consequently, therapeutic interventions that target hepatic lipid metabolism and inflammatory response pathways hold considerable promise for the treatment of NAFLD. Furthermore, there is a close link between the gut microbiota (GM) and host health. GM and its metabolites can rely on multiple complex pathways to be deeply involved in the occurrence and development of NAFLD, which is associated with a variety of mechanisms. This makes it difficult to achieve satisfactory therapeutic efficacy of drugs targeting a single specific mechanism. In this context, natural products have the advantage of intervening in multiple targets and high safety. Consequently, an increasing number of researchers are considering natural products as a potential breakthrough point for the treatment of NAFLD. Notably, natural products influence intestinal mucosal permeability and metabolite production by regulating the abundance of beneficial flora in GM, which in turn regulates lipid metabolism to reduce hepatic steatosis and inhibit the progression of NAFLD. This paper reviews the research progress of natural products intervening in NAFLD through GM and its metabolites and lipid metabolism that has emerged in recent years, aiming to provide a basis for future natural product interventions in NAFLD.
Keywords: NAFLD; gut microbiota; lipid metabolism; natural products; probiotics.
Copyright © 2025 Zhang, Wang, Han, Song, Yang, Liang, Li and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

