Analysis of risk factors and the predictive value of a nomogram model for coronary heart disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 40552192
- PMCID: PMC12183190
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1558012
Analysis of risk factors and the predictive value of a nomogram model for coronary heart disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is associated with an elevated risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) due to a complex interplay of traditional cardiovascular risk factors and RA-specific mechanisms. This study aimed to identify key risk factors for CHD in RA patients and develop a nomogram model for individualized risk prediction.
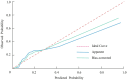
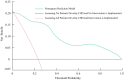
Methods: A retrospective study was conducted involving 258 RA patients, including 32 with CHD and 226 without CHD, admitted between January 2021 and August 2024. Demographic, clinical, and laboratory data were collected. Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified independent risk factors, which were incorporated into a nomogram model. The model's performance was evaluated using the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration plots, and decision curve analysis (DCA). Internal validation was performed using bootstrap resampling.
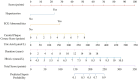
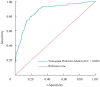
Results: Key risk factors for CHD in RA patients included hypertension, HbA1c, RA duration, carotid plaque burden, uric acid, and ECG abnormalities. The nomogram demonstrated excellent discriminative ability, with an area under the ROC curve (AUC) of 0.868 (95% CI: 0.819-0.916) and robust calibration (P = 0.908). Internal validation confirmed its reliability (AUC = 0.866). DCA indicated that the nomogram provided superior clinical utility by optimizing the net benefit across a range of threshold probabilities.
Conclusions: This study identified hypertension, elevated HbA1c, prolonged RA duration, carotid plaque burden, increased uric acid levels, and ECG abnormalities as significant risk factors for CHD in RA patients. A nomogram prediction model incorporating these factors was developed, exhibiting outstanding discriminatory and calibration capabilities.
Keywords: coronary heart disease; nomogram model; predictive analysis; rheumatoid arthritis; risk factors.
© 2025 Che, Zhao, An, Wang, Guo and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

