Impacts of proactive personality on students' academic achievement: a moderated mediation model
- PMID: 40552205
- PMCID: PMC12183227
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1596032
Impacts of proactive personality on students' academic achievement: a moderated mediation model
Abstract
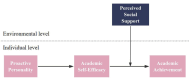
Introduction: A proactive personality, characterized by an individual's tendency to take initiative and actively shape their environment, has been increasingly recognized as a critical factor in academic success. Drawing on Job Demands-Resources (JD-R) theory and proactive motivation frameworks, this study investigates the relationship between proactive personality and academic achievement, focusing on the mediating role of academic self-efficacy and the moderating role of perceived social support.
Method: Data on proactive personality, academic self-efficacy, perceived social support, and academic achievement were gathered through WJX, yielding a total of 1,153 completed questionnaires. Statistical analyses were performed using SPSS and Mplus software, including correlation analysis, principal component analysis, t-tests, and parametric statistics.
Results: Results indicate that proactive personality positively predicts academic achievement, with academic self-efficacy serving as a significant mediator. Furthermore, perceived social support moderates this relationship, enhancing the positive effects of proactive personality on academic achievement through strengthened self-efficacy.
Discussion: The study highlight the importance of fostering proactive behaviors and providing robust social support systems in educational settings to promote students' academic success.
Keywords: academic achievement; academic self-efficacy; perceived social support; proactive personality; student.
Copyright © 2025 Liu, Lin, Jin, Li, Fu and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The impact of academic burnout on academic achievement: a moderated chain mediation effect from the Stimulus-Organism-Response perspective.Front Psychol. 2025 Jun 5;16:1559330. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1559330. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40538475 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of family support on junior high school students' engagement in physical education-A moderated chain mediation model.Front Psychol. 2025 Aug 4;16:1606642. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1606642. eCollection 2025. Front Psychol. 2025. PMID: 40831488 Free PMC article.
-
Male student nurses need more support: Understanding the determinants and consequences of career adaptability in nursing college students.Nurse Educ Today. 2020 Aug;91:104435. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2020.104435. Epub 2020 May 11. Nurse Educ Today. 2020. PMID: 32521422
-
The educational effects of portfolios on undergraduate student learning: a Best Evidence Medical Education (BEME) systematic review. BEME Guide No. 11.Med Teach. 2009 Apr;31(4):282-98. doi: 10.1080/01421590902889897. Med Teach. 2009. PMID: 19404891
-
Later school start times for supporting the education, health, and well-being of high school students.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 3;7(7):CD009467. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009467.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28670711 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Critical thinking disposition or proactive personality as predictors of academic resilience in nursing students.BMC Med Educ. 2025 Aug 25;25(1):1195. doi: 10.1186/s12909-025-07795-3. BMC Med Educ. 2025. PMID: 40855429 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bagozzi R. P., Yi Y. (1988). On the evaluation of structural equation models. J. Acad. Mark. Sci. 16, 74–94. 10.1007/BF02723327 - DOI
-
- Bagozzi R. P., Yi Y., Phillips L. W. (1991). Assessing construct validity in organizational research. Adm. Sci. Q. 36, 421–458. 10.2307/2393203 - DOI
-
- Bakker A. B., Demerouti E. (2007). The job demands-resources model: state of the art. J. Manage. Psychol. 22, 309–328. 10.1108/02683940710733115 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources