Telomere length and skin cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 40552254
- PMCID: PMC12183780
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2025.15141
Telomere length and skin cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
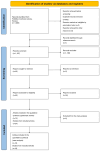
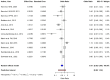
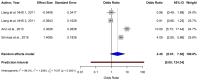
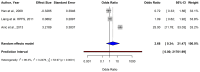
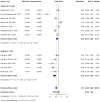
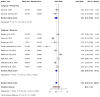
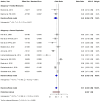
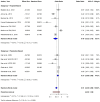
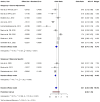
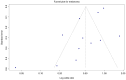
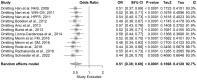
Skin cancer is one of the most prevalent types of cancer worldwide, with its global incidence rising despite prevention efforts. Telomere length (TL) has emerged as a potential biomarker for cancer risk; however, its relationship with skin cancer risk remains incompletely understood. To explore the association between TL and the risk of melanoma, basal cell carcinoma (BCC) and squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), a systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted. Longer TL was significantly associated with an increased risk in melanoma (pooled odds ratio: 0.51; 95% confidence interval: 0.38-0.69; P<0.0001). A significant association between longer TL and increased melanoma risk was identified in both familial melanoma and the general population. Subgroup analyses revealed consistent associations across sex, population source and adjustments for confounding factors. Geographic stratification indicated stronger associations in studies conducted in the USA compared with those from European populations. A meta-analysis of BCC and SCC studies did not achieve statistical significance, although qualitative synthesis suggested a potential association between shortened TL and increased risk. The significant association of longer TL and increased melanoma risk diverges from the conventional hypothesis that telomere shortening elevates cancer risk, highlighting a cancer-type specific telomeric relationship. The inconclusive findings for BCC and SCC underscore the necessity for further detailed investigation. Large-scale prospective studies with standardized methodologies are imperative to validate these findings and explore the underlying mechanisms. The present findings suggested that TL could potentially serve as a valuable biomarker for melanoma risk stratification in dermatologic oncology.
Keywords: basal cell carcinoma; biomarker; cancer; melanoma; skin cancer; squamous cell carcinoma; telomere biology; telomere length.
Copyright: © 2025 Andreikos and Spandidos.
Conflict of interest statement
DAS is the Editor-in-Chief for the journal, but had no personal involvement in the reviewing process, or any influence in terms of adjudicating on the final decision, for this article. The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
St Andrews Referral Delay in Skin Cancer (StARDISC): a study of keratinocyte skin cancer time to treatment, growth, invasiveness, British Association of Dermatologists risk factors and excision adequacy.Br J Dermatol. 2025 Jun 20;193(1):157-166. doi: 10.1093/bjd/ljaf097. Br J Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 40080699
-
Selenium for preventing cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 29;1(1):CD005195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005195.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29376219 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous magnesium sulphate and sotalol for prevention of atrial fibrillation after coronary artery bypass surgery: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2008 Jun;12(28):iii-iv, ix-95. doi: 10.3310/hta12280. Health Technol Assess. 2008. PMID: 18547499
-
Effectiveness and safety of vitamin D in relation to bone health.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007 Aug;(158):1-235. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2007. PMID: 18088161 Free PMC article.
-
A rapid and systematic review of the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of topotecan for ovarian cancer.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(28):1-110. doi: 10.3310/hta5280. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11701100
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
