Horseradish Peroxidase-Catalyzed Degradation of Reactive Blue 171 Dye
- PMID: 40552342
- PMCID: PMC12184795
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.5c01374
Horseradish Peroxidase-Catalyzed Degradation of Reactive Blue 171 Dye
Abstract
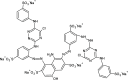
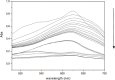
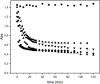
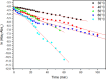
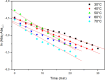
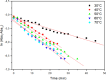
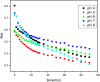
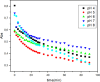
Despite establishing covalent bonds with cellulose, significant amounts of reactive dyes remain unfixed and are lost through secondary reactions during cellulosic fiber dyeing, ultimately entering textile wastewater and making additional treatment necessary. In this work, the kinetics of the biocatalytic degradation of the textile dye Reactive Blue 171 with horseradish peroxidase (HRP PeO 906) with an activity of 2009.2 kU/g was studied. The influence of temperature (in the range of 30-70 °C), pH (in the range of 4-8), the amount of biocatalyst (1, 2, and 3 mg), and hydrogen peroxide concentration (up to 0.3%) used in the process was evaluated. Biodegradation was monitored by the disappearance of the maximum absorption band of the dye at 625 nm. Biodegradation of Reactive Blue 171 followed first-order kinetics with rate constants ranging from 1.538 × 10-2 min-1 (30 °C) to 7.514 × 10-2 min-1 (70 °C) and R 2 ≥ 0.998. The best result observed for the biodegradation of Reactive Blue 171 was obtained at 40 °C when 0.1 g L-1 of dye, 3 mg of enzyme, and 0.3% H2O2 were used. Under these conditions activation parameters were determined as E a = 13.24 kJ mol-1(r 2 = 0.9919), ΔH # = 10.55 kJ mol-1 (r 2 = 0.9717), ΔG # medium = 14.09 kJ mol-1, and ΔS # medium = 0.109 kJ K-1 mol-1, achieving a decolorization of 81.40% after 120 min. Biodegradation involved low energy variation and was favored by increases in temperature and biocatalyst concentration. In the investigated pH range, the highest dye degradation was observed at pH 4 and 5. The obtained decolorization results of Reactive Blue 171 with HRP and H2O2 indicate that the biodegradation of textile dyes is a viable and sustainable method.
© 2025 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Figures

References
-
- Rodriguez-Mozaz S., Ricart M., Köck-Schulmeyer M., Guasch H., Bonnineau C., Proia L., de Alda M. L., Sabater S., Barceló D.. Pharmaceuticals and Pesticides in Reclaimed Water: Efficiency Assessment of a Microfiltration–Reverse Osmosis (MF–RO) Pilot Plant. J. Hazard Mater. 2015;282:165–173. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Singh K., Arora S.. Removal of Synthetic Textile Dyes From Wastewaters: A Critical Review on Present Treatment Technologies. Crit Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011;41(9):807–878. doi: 10.1080/10643380903218376. - DOI
-
- Behera M., Nayak J., Banerjee S., Chakrabortty S., Tripathy S. K.. A Review on the Treatment of Textile Industry Waste Effluents towards the Development of Efficient Mitigation Strategy: An Integrated System Design Approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021;9(4):105277. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2021.105277. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
