Prognostic Value of the TLM3 Biomarker Panel for Early Fibrosis Development in MASLD Within the General Population
- PMID: 40552595
- PMCID: PMC12186288
- DOI: 10.1111/liv.70169
Prognostic Value of the TLM3 Biomarker Panel for Early Fibrosis Development in MASLD Within the General Population
Abstract
Background & aims: Fibrotic MASLD is associated with increased morbidity and mortality, often remaining asymptomatic until advanced stages of disease. Predicting fibrosis onset and progression would improve risk stratification and treatment allocation. This study aims to investigate whether a previously identified fibrosis biomarker panel for active fibrogenesis (TLM3) can serve as a prognostic marker panel for fibrosis development in a population at cardiometabolic risk of fibrotic MASLD.
Methods: The temporal dynamics of a molecular fibrosis gene expression signature associated with histologically proven fibrosis development was investigated in a diet-induced MASLD mouse model (LDLr-/-.Leiden). The corresponding proteins were measured in baseline serum from individuals at risk of MASLD from the general population HELIUS-cohort and correlated with established fibrosis proxies (ELF, VCTE and FIB4) at 7 years follow-up.
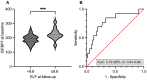
Results: The molecular fibrosis gene expression signature was upregulated in a murine MASLD model before the onset of histopathological features of fibrosis. In humans, serum levels of IGFBP7, Ssc5D, Sema4D, VCAN, THBS1 and TNC at baseline correlated with fibrosis proxies at follow-up. IGFBP7 at baseline was able to predict new onset fibrosis, defined as ELF ≥ 9.8 at follow-up in participants with ELF < 9.8 at baseline, with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.79 (95% CI: 0.64-0.94).
Conclusion: Together, these findings indicate the potential predictive capacity of the TLM3 biomarker panel in early stages of MASLD-fibrosis, both in a murine model as well as in individuals from the general population at risk of MASLD.
Keywords: MASH; biomarker; disease progression; fibrogenesis; non‐invasive.
© 2025 The Author(s). Liver International published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
M.N. is on the Scientific Advisory Board of Caelus Pharmaceuticals and Advanced Microbiome Interventions, the Netherlands. However, none of these bear direct relevance to the current manuscript. Other authors have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Platelet Functional Profile Is Altered in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease.Liver Int. 2025 Aug;45(8):e70231. doi: 10.1111/liv.70231. Liver Int. 2025. PMID: 40719417 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of the prevalence of MASLD, MASH and liver fibrosis in a Dutch bariatric cohort.PLoS One. 2025 Jun 24;20(6):e0324813. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0324813. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40554612 Free PMC article.
-
Screening for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease-Related Advanced Fibrosis in Diabetology: A Prospective Multicenter Study.Diabetes Care. 2025 Jun 1;48(6):877-886. doi: 10.2337/dc24-2075. Diabetes Care. 2025. PMID: 39887699
-
Adefovir dipivoxil and pegylated interferon alfa-2a for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B: a systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Aug;10(28):iii-iv, xi-xiv, 1-183. doi: 10.3310/hta10280. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16904047
-
NIH Consensus Statement on Management of Hepatitis C: 2002.NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002 Jun 10-12;19(3):1-46. NIH Consens State Sci Statements. 2002. PMID: 14768714
References
-
- Hardy T., Oakley F., Anstee Q. M., and Day C. P., “Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathogenesis and Disease Spectrum,” Annual Review of Pathology 11 (2016): 451–496. - PubMed
-
- Nabi O., Lacombe K., Boursier J., Mathurin P., Zins M., and Serfaty L., “Prevalence and Risk Factors of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Advanced Fibrosis in General Population: The French Nationwide NASH‐CO Study,” Gastroenterology 159, no. 2 (2020): 791–793.e2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

