Enterovirus C recombination groups: RNA sequence similarity and the viral polymerase underpin sexual replication mechanisms
- PMID: 40552818
- PMCID: PMC12282145
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00434-25
Enterovirus C recombination groups: RNA sequence similarity and the viral polymerase underpin sexual replication mechanisms
Abstract
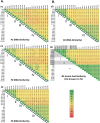
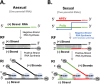
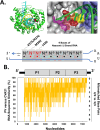
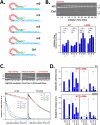
Enteroviruses frequently recombine with one another in nature; however, it is unclear how viral replication machinery can distinguish between related and unrelated partners during recombination. We hypothesize that viral RNA recombination involves two parental RNA templates, nascent RNA products, and their dynamic interactions with the viral polymerase-a sexual replication strategy. When nascent RNA products move from one parental RNA template to another, RNA sequence similarity may be an important factor underpinning the mechanism and efficiency of recombination. To test this hypothesis, we focused on recombination between two related group C enteroviruses, poliovirus and Coxsackievirus A21 (CVA21), using bioinformatic, biological, and biochemical approaches. Bioinformatic analyses comparing 22 prototypical group C enteroviruses delineated four recombination groups where viruses in each group exhibit high RNA sequence and amino acid similarity in their polymerase genes. ClickSeq and ViReMa methods detect recombinant forms of poliovirus with P3 genes from CVA21, analogous to recombinant circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses (cVDPV). Biochemical assays show that poliovirus and CVA21 polymerases can detect mismatched base pairs as they traverse an extended primer grip surface adjacent to the active site. Mismatched base pairs in the -2 and -3 positions destabilize polymerase elongation complexes, consistent with the predicted role of RNA sequence similarity in recombination. Two subgroup-specific genetic elements, upstream open-reading frames (uORFs) and RNase L competitive inhibitor RNAs (RNase L ciRNAs), reinforce the existence and biological relevance of enterovirus C recombination groups. Altogether, our observations suggest that enterovirus RNA replication machinery can distinguish between related and unrelated partners during recombination.
Importance: Viral RNA recombination transforms live-attenuated polioviruses into neurovirulent circulating vaccine-derived polioviruses, complicating the planned eradication of poliovirus. When humans are co-infected with poliovirus and related non-polio enteroviruses, viral replication machinery can produce recombinant viruses. However, who recombines with whom? What factors determine whether two distinct viruses can produce recombinant progeny that are fit for transmission from person to person? In this study, we clarify which viruses recombine with one another in nature and further elucidate the mechanisms by which the viral polymerase distinguishes between related and unrelated RNA templates-a sexual form of replication. Understanding these mechanisms could lead to better strategies for virus control and/or eradication.
Keywords: RDRP; RNA recombination; RNA-dependent RNA polymerase; enterovirus; picornavirus; poliovirus; positive-strand RNA virus.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Routh is a co-founder and owner of ClickSeq Technologies LLC, a Next-Generation Sequencing provider offering ClickSeq kits and services including the methods described in this article. The other authors have no conflicts to declare.
Figures




References
-
- Lulla V, Dinan AM, Hosmillo M, Chaudhry Y, Sherry L, Irigoyen N, Nayak KM, Stonehouse NJ, Zilbauer M, Goodfellow I, Firth AE. 2019. An upstream protein-coding region in enteroviruses modulates virus infection in gut epithelial cells. Nat Microbiol 4:280–292. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0297-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

