Relationship of Prior Anticancer Treatments with Palbociclib Clinical Outcomes in Patients with HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer in Real-World Settings
- PMID: 40553419
- PMCID: PMC12307473
- DOI: 10.1007/s11523-025-01158-0
Relationship of Prior Anticancer Treatments with Palbociclib Clinical Outcomes in Patients with HR+/HER2- Advanced Breast Cancer in Real-World Settings
Abstract
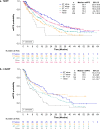
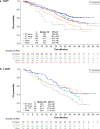
Background: In the real-world POLARIS study, patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+)/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative (HER2-) advanced/metastatic breast cancer (ABC) who had received palbociclib + endocrine therapy (ET) had a median real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS) of 20.9 months in the first line of therapy (1LOT) and 13.5 months in second or later LOTs (≥ 2LOT).
Objective: The aim of this study is to assess the relationship of prior anticancer treatments with clinical outcomes.
Patients and methods: Kaplan-Meier estimates of rwPFS and overall survival (OS) are described by prior anticancer treatments in patients with HR+/HER2- ABC who received palbociclib + ET.
Results: A total of 1250 patients received ≥ 1 palbociclib dose (1LOT: 901 [72.1%]; ≥ 2LOT: 349 [27.9%]). In the 1LOT group, 563 (62.5%) had received prior (neo)adjuvant treatments: 24.3% ET alone, 26.6% chemotherapy alone, 45.5% ET + chemotherapy, and 3.6% other treatments; both median rwPFS and OS were numerically longer in patients who had received ET alone (30.4 months and not reached, respectively) and had had no prior treatment (23.7 and 53.3 months, respectively) than in patients with prior chemotherapy alone (15.9 and 38.4 months, respectively). In the ≥ 2LOT group, patients with prior ET alone (21.5%; 19.8 months) or chemotherapy alone (16.6%; 15.5 months) in the (neo)adjuvant and/or metastatic setting had numerically longer median rwPFS than those with prior ET + chemotherapy (41.3%; 11.6 months); OS was comparable regardless of prior treatment.
Conclusions: Patients with HR+/HER2- ABC who had received ET alone prior to palbociclib tended to have better clinical outcomes, while those with prior chemotherapy had less clinical benefit.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT03280303.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Funding: This study was sponsored by Pfizer Inc. Conflicts of interest: Gabrielle Rocque received research funding from Genentech, Pfizer Inc, and Daiichi Sankyo and consulting fees from Pfizer Inc, Gilead, and Armada. Joanne L. Blum reports acting as a paid consultant for Pfizer Inc and Tempus and on the speaker’s bureau of Pfizer Inc and Tempus. Yan Ji received compensation for being on advisory boards for Janssen, AstraZeneca, and BeiGene. Timothy Pluard reports acting as a paid consultant for Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Jazz Pharmaceutical, Daiichi, and Gilead; receiving research funding (institution) from Daiichi Sankyo, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer Inc, Sermonix, Scorpion, Merck, DualityBio, and Arvinas; participating in the speaker’s bureau of Gilead, AstraZeneca, and Stemline. John Migas reports contracted research (clinical trials) paid to his institution (Pfizer Inc, AstraZeneca, Jazz Pharmaceuticals). Shailendra Lakhanpal reports no conflicts of interest. Erin Jepsen reports being an employee of Novant Health Cancer Institute. Yao Wang, Zhe Zhang, and Eric Gauthier report being employees of and stockholders in Pfizer Inc. Monica Z. Montelongo reports being an employee of ICON and was funded by Pfizer Inc to conduct the study. Debu Tripathy reports contracted research (clinical trials) paid to his institution from Novartis, Pfizer Inc, and Polyphor and paid consultancy for AstraZeneca, OncoPep, GlaxoSmithKline, Gilead, Personalis, Sermonix, Pfizer Inc, Puma Biotechnology, Roche, Novartis, Menarini-Stemline, BeiGene, AMBRX, and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. Data availability: Upon request, and subject to review, Pfizer will provide the data that support the findings of this study. Subject to certain criteria, conditions, and exceptions, Pfizer may also provide access to the related individual deidentified participant data. See https://www.pfizer.com/science/clinical-trials/data-and-results for more information. Ethics approval: The study was conducted in accordance with local regulatory and legal requirements and was reviewed and approved by applicable local institutional review boards or independent ethics committees. The study was performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. Consent to participate: All patients provided written informed consent before participating in the study. Consent for publication: Not applicable. Code availability: Not applicable. Author contributions: Conception/design: GBR, EG, and DT. Provision of study material or patients: GBR, JLB, TP, and DT. Collection and/or assembly of data: MZM. Data analysis and interpretation: GBR, JLB, MZM, ZZ, EG, and DT. Manuscript drafting and revision: all authors. Final approval of submitted manuscript: all authors.
Figures
References
-
- Deluche E, Antoine A, Bachelot T, Lardy-Cleaud A, Dieras V, Brain E, et al. Contemporary outcomes of metastatic breast cancer among 22,000 women from the multicentre ESME cohort 2008–2016. Eur J Cancer. 2020;129:60–70. 10.1016/j.ejca.2020.01.016. - PubMed
-
- McAndrew NP, Finn RS. Clinical review on the management of hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. JCO Oncol Pract. 2022;18(5):319–27. 10.1200/op.21.00384. - PubMed
-
- Gennari A, André F, Barrios CH, Cortés J, de Azambuja E, DeMichele A, et al. ESMO clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, staging and treatment of patients with metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2021;32(12):1475–95. 10.1016/j.annonc.2021.09.019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

