Long-term outcomes of patients with refractory cytopenia of childhood under observation only
- PMID: 40554414
- PMCID: PMC12395045
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025016136
Long-term outcomes of patients with refractory cytopenia of childhood under observation only
Abstract
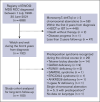
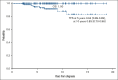
Refractory cytopenia of childhood (RCC) describes an entity of well-recognized bone marrow failure defined by persistent cytopenia, dysplastic changes, and a unique histopathological pattern in the bone marrow. Although hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) is generally indicated for patients with severe cytopenia or abnormal karyotype, a subset of patients with RCC may be candidates for an observational approach. We evaluated the long-term outcome of patients with RCC without evidence of a genetic predisposition who had a normal karyotype and had not received HSCT or immunosuppressive therapy within 2 years from diagnosis. The median age at diagnosis of the 100 patients analyzed was 10.9 years (range 1.4-17.3); 84% presented with a hypocellular bone marrow. Clonal evolution with abnormal karyotype occurred in 3 patients (3%), and 1 case progressed to myelodysplastic syndrome with excess blasts. Three patients (3%) developed paroxysmal nocturnal hematuria. Overall, 9 patients (9%) received HSCT, and the 5- and 10-year HSCT-free survival was 94% and 88%, respectively. At last follow-up, all patients were alive with a median follow-up time of 7.2 years. These results indicate that an observational approach is safe for selected patients with RCC with a normal karyotype after an exclusion of a germ line predisposition syndrome. However, persistence of cytopenia in most of these patients underscores the importance of long-term surveillance and transition to adult hematology care. This trial was registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT00047268 and #NCT00662090.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors declare no competing financial interests.
The current affiliation for G.G. is Amedes Genetics, Hannover, Germany.
Figures
References
-
- Steensma DP. The clinical challenge of idiopathic cytopenias of undetermined significance (ICUS) and clonal cytopenias of undetermined significance (CCUS) Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2019;14(6):536–542. - PubMed
-
- DeZern AE, Malcovati L, Ebert BL. CHIP, CCUS, and other acronyms: definition, implications, and impact on practice. Am Soc Clin Oncol Educ Book. 2019;39:400–410. - PubMed
-
- Baumann I, Führer M, Behrendt S, et al. Morphological differentiation of severe aplastic anaemia from hypocellular refractory cytopenia of childhood: reproducibility of histopathological diagnostic criteria. Histopathology. 2012;61(1):10–17. - PubMed
-
- Rudelius M, Weinberg OK, Niemeyer CM, Shimamura A, Calvo KR. The International Consensus Classification (ICC) of hematologic neoplasms with germline predisposition, pediatric myelodysplastic syndrome, and juvenile myelomonocytic leukemia. Virchows Arch. 2023;482(1):113–130. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical