Real-world data for tisagenlecleucel in patients with R/R B-ALL: subgroup analyses from the CIBMTR registry
- PMID: 40554426
- PMCID: PMC12552949
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2025015881
Real-world data for tisagenlecleucel in patients with R/R B-ALL: subgroup analyses from the CIBMTR registry
Abstract
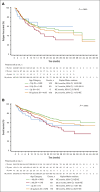
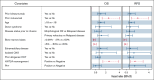
Since the first approval of tisagenlecleucel in 2017, pediatric and young adult patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) may receive this CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy. We report real-world data from the Center for International Blood and Marrow Transplant Research (>2.5 years of follow-up). As of 4 May 2022, 768 patients with B-ALL had received tisagenlecleucel. Patients aged ≥18 and <18 years of age (including those <3 years) were treated during first relapse (26.6% and 26.7% [<3 years, 44.8%], respectively) or primary refractory disease (12.4% and 12.1% [<3 years, 15.5%], respectively) with 17.6% and 11.6% (<3 years, 13.8%), respectively, having high disease burden (≥50% bone marrow [BM] blasts) and 20.2% and 20.2% (<3 years, 13.8%), respectively, having low disease burden (>0 to <5% BM blasts). Among patients with ≥12 months postinfusion follow-up (n = 578; median follow-up, 32.1 months), the best overall response of complete remission/complete remission with incomplete blood count recovery was 86.0%. The 12-month relapse-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) were 61.8% and 79.4%, respectively, whereas the 24-month RFS and OS were 50.3% and 63.8%, respectively. Age (<18 years) and disease burden (<50% BM blasts) were associated with better outcomes. Previous inotuzumab therapy and KMT2A rearrangement were associated with worse outcomes. Older patients (≥18 years) experienced a higher rate of any-grade cytokine release syndrome (CRS) associated with higher disease burden before infusion. Any-grade CRS and neurotoxicity were lower in patients aged <3 years. Extended follow-up continues to demonstrate high rates of RFS and favorable safety in this population.
© 2025 American Society of Hematology. Published by Elsevier Inc. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0), permitting only noncommercial, nonderivative use with attribution. All other rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure: K.J.C. reports serving as a consultant for Novartis; participating as board member and shareholder for Turn Bio and PromiCell; and research funding from Novartis, Cellectis, and Atara Bio. E.M.H.’s spouse reports participating in a speaker's bureau for Boehringer Ingelheim; honoraria from Vida Diagnostics; and participating on a scientific advisory committee for Polarean. S.H.C.B.’s spouse reports former employment for Alexion and Takeda Pharmaceuticals and holds Takeda and AstraZeneca stock and stock options. S.N. reports participating in ad hoc advisory boards for A2 Bio, Legend Biotech, Kite/Gilead, Iovance, SmartImmune, and GlaxoSmithKline. C.L.P. reports serving as a member on the board of directors or advisory committees for Novartis. M.A.P. reports participating in scientific advisory boards for Medexus, Equillium, Mesoblast, and Novartis; participating in sponsored invited educational talks for Novartis and Miltenyi Biotec; and study support from Miltenyi Biotec and Adaptive Biotechnologies. R.H.R. reports honoraria from Novartis; research funding from Tessa Therapeutics; and serving as a consultant for Pfizer. M.C.P. reports research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb, Novartis, Kite Pharma, and GlaxoSmithKline; and serving as a consultant for Bristol Myers Squibb. R.T., J.W., and R.R. report current employment with Novartis. J.K. reports serving as a consultant for Kite/Gilead and Novartis. E.G. reports participating in scientific advisory boards for Syndax and Jazz Pharmaceuticals. S.A.G. reports research and/or clinical trial support from Novartis, Servier, Vertex, and Kite Pharma; and participating in study steering committees or serving as a consultant or on scientific advisory boards for Novartis, Allogene, Cellectis, CRISPR/Vertex, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, TCR2, Allogene, BioLineRx, Mckesson, and Cabaletta. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

