Systems thinking with active implementation research (STAIR): Protocol for a school-based randomised control trial for childhood obesity prevention
- PMID: 40554468
- PMCID: PMC12186940
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325853
Systems thinking with active implementation research (STAIR): Protocol for a school-based randomised control trial for childhood obesity prevention
Abstract
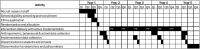
Introduction: This paper presents the protocol for the effectiveness-implementation trial: Systems Thinking with Active Implementation Research (STAIR) for childhood obesity prevention. STAIR's objective is to protect primary school children in Victoria, Australia from unhealthy weight and test implementation strategies for sustaining healthy school environments. STAIR is a 3-year cluster-randomised controlled trial with repeat-cross-sectional child-level data collection utilising an effectiveness-implementation type-1 hybrid design. Schools will be recruited from non-metropolitan government primary schools in Southwest Victoria, Australia, with consenting schools (target = 28) randomly assigned (1:1) to intervention or control, and students in grades 1-6 (n = 3000-6000) recruited using an opt-out approach.
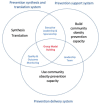
Intervention: The intervention, co-designed by each school community, will involve multi-step group model building and action formulation process using community-based systems dynamics and baseline data (i.e., child weight status, HRQoL, health behaviours, and school environment characteristics). Implementation strategies will be guided by an active implementation framework, and coordinated by a leadership team of school representatives, community partners, and researchers.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: Primary outcomes are to measure (1) change in standardised body mass index (z-BMI) between intervention and control groups after three year and (2) change in acceptance and adoption of STAIR interventions and support. Secondary outcomes include differences in obesity prevalence, health behaviour measures and HRQoL, between intervention and control groups after three years. Implementation outcomes will focus on strategy effectiveness, acceptability, and utilisation. Secondary data will be collected from schools and partner organisations. An economic evaluation will assess the cost-effectiveness of intervention and implementation support.
Conclusion: STAIR aims to create lasting changes in schools to prevent childhood obesity by supporting healthy environments and providing insights into interventions' cost-effectiveness and feasibility. The findings will guide policymakers and educational institutions in adopting sustainable health promotion strategies.
Trial registration: ANZCTR-ACTRN12624000461594p.
Copyright: © 2025 Jackson et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Chan M. WHO director-general opens a meeting of the childhood obesity commission. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2014. 1 p.
-
- Australian Institute of Health and Welfare. Overweight and obesity among Australian children and adolescents. Canberra, Australia: AIHW; 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical