Attentional biases, as measured by motion-induced blindness, are linked to schizophrenia traits
- PMID: 40554481
- PMCID: PMC12186884
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0325609
Attentional biases, as measured by motion-induced blindness, are linked to schizophrenia traits
Abstract
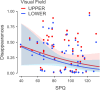
Typically, people demonstrate a small attentional bias towards the left visual field. This bias has not consistently been observed in schizophrenia. Schizophrenia has been thought to be linked to a top visual field bias, due to an impaired dorsal stream found in those individuals. Here we assessed left/right and upper/lower spatial biases measuring perceptual disappearances in a motion-induced blindness (MIB) task and link those to schizophrenia traits. The sample were consisted of first year psychology students (N = 54; 22 males, 31 females, and 1 prefer not to say; age 18-54 years; median age = 23). Schizophrenia traits were measured using the schizotypal personality questionnaire (SPQ) and perceptual aberration scale (PAS). We found that higher SPQ scores correlated with a top field bias. Higher interpersonal scores (an SPQ subscore) linked to a right field, and so did PAS (p = .007). Higher cognitive-perceptual scores linked to a left field bias. Taken together, this study supports a complex relation between spatial attention and schizophrenia traits in MIB, in which a top field bias may reflect an impaired dorsal stream. A possible implication of these findings is that MIB may serve as a potential tool for screening early schizophrenia traits.
Copyright: © 2025 Paton, van Boxtel. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Intravenous versus inhalational maintenance of anaesthesia for postoperative cognitive outcomes in elderly people undergoing non-cardiac surgery.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Aug 21;8(8):CD012317. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012317.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30129968 Free PMC article.
-
Interventions targeted at women to encourage the uptake of cervical screening.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Sep 6;9(9):CD002834. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002834.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34694000 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Antipsychotics for schizophrenia spectrum disorders with catatonic symptoms.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jul 12;7(7):CD013100. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013100.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35844143 Free PMC article.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. 5th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Publishing. 2013.
-
- Winterstein BP, Willse JT, Kwapil TR, Silvia PJ. Assessment of Score Dependability of the Wisconsin Schizotypy Scales Using Generalizability Analysis. J Psychopathol Behav Assess. 2010;32(4):575–85. doi: 10.1007/s10862-010-9181-x - DOI
-
- World Health Organization. Schizophrenia. Geneva: World Health Organization. 2022.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

