Prognostic nutritional index in the prediction of adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Urumqi, China: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 40555440
- PMCID: PMC12198849
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-099750
Prognostic nutritional index in the prediction of adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Urumqi, China: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Objective: Prognostic nutritional index (PNI) is an index for assessing nutritional and immune status. The aim of this study is to investigate the predictive value of PNI for long-term major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Design, setting and participants: This retrospective cohort study analysed 1582 STEMI patients with T2DM who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention from January 2015 to June 2023 in Urumqi, China. Patients were followed up for MACCE.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: The primary endpoint was new-onset MACCE including all-cause death, non-fatal MI and non-fatal stroke.
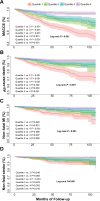
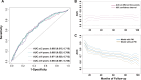
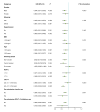
Results: This study ultimately included 1582 patients for analysis with a median follow-up period of 48 months (IQR: 24-84 months) and 282 patients (17.8%) developed MACCE. Of them, 138 (8.7%), 84 (5.3%) and 60 (3.8%) patients developed all-cause death, a non-fatal MI and a non-fatal stroke, respectively. Incidences of MACCE and all-cause death conversely correlated with PNI. Kaplan-Meier curves showed a significant difference in all components of MACCE between PNI quartiles (p<0.001). The multivariate Cox regression analysis revealed that PNI was an independent predictor of MACCE (adjusted HR 0.95, 95% CI 0.93 to 0.97, p<0.001) and all-cause death (adjusted HR 0.93, 95% CI 0.90 to 0.97, p<0.001). The optimal PNI cut-off for predicting MACCE and all-cause death was 45.10 and 45.09, respectively. Moreover, the addition of PNI to the traditional prognostic model for MACCE improved the C-statistic value (p<0.001).
Conclusions: PNI, a simple and easily obtainable index, was independently associated with MACCE and all-cause death in this study. Lower PNI levels were significantly linked to an increased risk of long-term MACCE, especially in male, elderly patients and those with higher glycosylated haemoglobin and low- density lipoprotein cholesterol levels.
Keywords: Diabetic nephropathy & vascular disease; Ischaemic heart disease; Myocardial infarction.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Effects of a gluten-reduced or gluten-free diet for the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Feb 24;2(2):CD013556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35199850 Free PMC article.
-
Association between adjusted atherogenic index of plasma and major adverse cardiovascular events after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with STEMI: a prospective observational study in China.BMJ Open. 2025 Aug 21;15(8):e096065. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-096065. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40840987 Free PMC article.
-
Triglyceride-glucose index as a predictor of cardiac adverse events in acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention: role of diabetes.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):514. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04191-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39333881 Free PMC article.
-
Complete versus culprit-only revascularisation in ST elevation myocardial infarction with multi-vessel disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 May 3;5(5):CD011986. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011986.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28470696 Free PMC article.
-
Smoking cessation for secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 8;8(8):CD014936. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD014936.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35938889 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
