Rice-derived recombinant human serum albumin as an alternative to human plasma for patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis: a randomised, double-blind, positive-controlled and non-inferiority trial
- PMID: 40555465
- PMCID: PMC12418551
- DOI: 10.1136/gutjnl-2025-335577
Rice-derived recombinant human serum albumin as an alternative to human plasma for patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis: a randomised, double-blind, positive-controlled and non-inferiority trial
Abstract
Background: Despite inadequate supply and potential contamination risk, human plasma has remained the only source for human serum albumin (pHSA) intravenous administration since the 1940s.
Objective: We sought to establish the safety and efficacy of OsrHSA, a recombinant HSA from bioengineered Oryza sativa (rice).
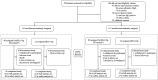
Design: In this multicentre, randomised, double-blind and positive-controlled study, patients with decompensated liver cirrhosis and serum albumin ≤30 g/L were recruited from 22 centres in China. The patients were randomly assigned to OsrHSA or pHSA (4:1) to once-daily intravenous injection (10 g or 20 g) until their serum albumin level reached 35 g/L, for a maximum of 2 weeks, with 2 weeks of follow-up. The primary outcome was the proportion of patients to reach a serum albumin level of 35 g/L (non-inferiority margin <-0.20). Outcomes were evaluated in patients who received the study drug and had at least one post-baseline serum albumin value (full analysis set, FAS). Safety was evaluated in all patients who received the study drug.
Results: Between 22 March 2021 and 2 June 2022, 220 patients received OsrHSA (n=175) or pHSA (n=45). 216 patients were included in the FAS (OsrHSA, n=171; pHSA, n=45). Primary outcome of OsrHSA (130/171, 76%) was non-inferior to pHSA (34/45, 75.6%) (difference=0.5%; lower limit of 97.5% CI=-0.119). There was no significant difference between all secondary outcomes of OsrHSA and pHSA. There were no drug-related serious adverse events.
Conclusions: Rice-derived HSA is non-inferior to plasma-derived HSA in efficacy and safety. This finding should be confirmed in phase 3 trial.
Trial registration number: NCT04835480.
Keywords: HEALTH ECONOMICS; LIVER CIRRHOSIS.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2025. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ Group.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: ZQ, HM, CYY and DY are employees of Healthgen Biotech. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Alexander MR, Ambre JJ, Liskow BI, et al. Therapeutic use of albumin. JAMA. 1979;241:2527–9. - PubMed
-
- Erstad BL. Viral infectivity of albumin and plasma protein fraction. Pharmacotherapy. 1996;16:996–1001. - PubMed
-
- Blood safety and availability. 2024. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/blood-safety-and-availa... Available.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
