Comparative efficacy and safety of daridorexant, lemborexant, and suvorexant for insomnia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
- PMID: 40555730
- PMCID: PMC12187915
- DOI: 10.1038/s41398-025-03439-8
Comparative efficacy and safety of daridorexant, lemborexant, and suvorexant for insomnia: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: In order to appraise the risk-benefit balance of the three available dual orexin receptor antagonists (DORAs; daridorexant, lemborexant, and suvorexant) for the management of adults with insomnia, we conducted a systematic review and random-effects model network meta-analysis.
Methods: Included were all published double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials of these agents. Outcomes included subjective time to sleep onset at month 1 (sTSO, primary), subjective total sleep time at month 1 (sTST, co-primary), subjective wake after sleep onset at month 1, Insomnia Severity Index scores at month 1, all-cause discontinuation, discontinuation due to adverse events, and the incidence of individual adverse events such as somnolence, dizziness, falls, headache, nasopharyngitis, and upper respiratory tract infection.
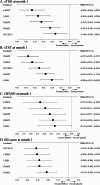
Results: This meta-analysis included eight trials (5198 adults, average age = 56.33 years, 67.84% female). The treatment arms included daridorexant 25 mg/day (DAR25), daridorexant 50 mg/day (DAR50), lemborexant 5 mg/day (LEM5), lemborexant 10 mg/day (LEM10), suvorexant 20 mg/day (15 mg/day for people ≥65years, SUV20/15), and placebo. All active-treatments outperformed placebo in terms of all efficacy outcomes. The standardized mean difference (95% CI) in primary outcomes ranged from; sTSO: -0.430 (-0.568, -0.292) for LEM10 to -0.164 (-0.296, -0.031) for SUV20/15 and sTST: -0.475 (-0.593, -0.357) for DRA50 to -0.206 ( -0.330, -0.082) for LEM5. An additional sensitivity analysis suggested that DRA25, LEM10, and SUV20/15 were associated with a higher incidence of somnolence compared to a placebo.
Conclusions: Considering that there is no evidence that DORAs are associated with physiological tolerance, withdrawal symptoms, or rebound insomnia when abruptly discontinued, and that sleep architecture is not adversely affected, the DORAs appear to be a favorable choice in managing insomnia disorder in adults.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have no competing interests to declare concerning this study. They also declare any potential competing interests that have arisen in the last 3 years. Prof. Kishi has received speaker’s honoraria from Eisai, Janssen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Meiji, Otsuka, Sumitomo, Takeda, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, Kyowa, Yoshitomi, and Viatris and research grants from Eisai, a Fujita Health University School of Medicine Research Grant, JSPS KAKENHI (19K08082 and 23K06998), Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (JP22dk0307107, JP22wm0525024, JP23dk0307122, and 24dk0307129), and the Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare (21GC1018). Dr. Ikuta has nothing to disclose. Prof. Citrome serves as consultant to AbbVie/Allergan, Acadia, Adamas, Alkermes, Angelini, Astellas, Avanir, Axsome, Biogen, BioXcel, Bristol-Myers Squibb /Karuna, Boehringer Ingelheim, Cadent Therapeutics, Cerevel, Clinilabs, COMPASS, Delpor, Eisai, Enteris BioPharma, HLS Therapeutics, Idorsia, INmune Bio, Impel, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Lundbeck, Luye, Lyndra, MapLight, Marvin, Medavante-ProPhase, Merck, Mitsubishi-Tanabe Pharma, Neumora, Neurocrine, Neurelis, Noema, Novartis, Noven, Otsuka, Ovid, Praxis, Recordati, Relmada, Reviva, Sage, Sumitomo/Sunovion, Supernus, Teva, University of Arizona, Vanda, Wells Fargo, and one-off ad hoc consulting for individuals/entities conducting marketing, commercial, or scientific scoping research; speaker for AbbVie/Allergan, Acadia, Alkermes, Angelini, Axsome, BioXcel, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Idorsia, Intra-Cellular Therapies, Janssen, Lundbeck, Neurocrine, Noven, Otsuka, Recordati, Sage, Sunovion, Takeda, Teva, and CME activities organized by medical education companies such as Medscape, NACCME, NEI, Vindico, and Universities and Professional Organizations/Societies; owns stocks (small number of shares of common stock): Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, J & J, Merck, Pfizer purchased >10 years ago, stock options: Reviva; and receives royalties/publishing income from Taylor & Francis (Editor-in-Chief, Current Medical Research and Opinion, 2022-date), Wiley (Editor-in-Chief, International Journal of Clinical Practice, through end 2019), UpToDate (reviewer), Springer Healthcare (book), Elsevier (Topic Editor, Psychiatry, Clinical Therapeutics). Dr. Sakuma has received speaker’s honoraria from daiichisankyo, Eisai, Janssen, Kyowa, Meiji, Otsuka, Sumitomo, and Takeda and has received a Fujita Health University School of Medicine Research Grant for Early-Career Scientists, Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B)(19K17099), Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C)(23K06998), and Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (JP22dk0307107 and JP23dk0307122). Dr. Hatano received the speaker’s honoraria from Meiji and Sumitomo, and has received Grant-in-Aid for Early-Career Scientists (23K14827). Dr. Hamanaka has received speaker’s honoraria from Meiji, Otsuka, and Sumitomo. Dr. Nishii has received speaker’s honoraria from Meiji, Otsuka, and Sumitomo. Prof. Iwata has received speaker’s honoraria from Eisai, Janssen, Meiji, Otsuka, Sumitomo, Takeda, Mitsubishi-Tanabe, and Viatris and research grants from Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Meiji, Otsuka, Sumitomo, Takeda, Tanabe-Mitsubishi, Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (B)(22H03003), and Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (JP22wm0425008).
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lemborexant vs suvorexant for insomnia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.J Psychiatr Res. 2020 Sep;128:68-74. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.05.025. Epub 2020 May 28. J Psychiatr Res. 2020. PMID: 32531478
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of dual orexin receptor antagonists lemborexant and daridorexant for the treatment of insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025 Aug;242(8):1693-1711. doi: 10.1007/s00213-025-06773-3. Epub 2025 Mar 25. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2025. PMID: 40133470
-
Clinical safety and narcolepsy-like symptoms of dual orexin receptor antagonists in patients with insomnia: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Sleep. 2024 Feb 8;47(2):zsad293. doi: 10.1093/sleep/zsad293. Sleep. 2024. PMID: 37950346
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of lemborexant 5 mg versus 10 mg for the treatment of insomnia: a systematic review.Neurol Sci. 2023 May;44(5):1533-1541. doi: 10.1007/s10072-023-06601-6. Epub 2023 Jan 12. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36633778
-
Suvorexant for insomnia: a systematic review of the efficacy and safety profile for this newly approved hypnotic - what is the number needed to treat, number needed to harm and likelihood to be helped or harmed?Int J Clin Pract. 2014 Dec;68(12):1429-41. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.12568. Epub 2014 Sep 18. Int J Clin Pract. 2014. PMID: 25231363
References
-
- Perlis ML, Posner D, Riemann D, Bastien CH, Teel J, Thase M. Insomnia. Lancet. 2022;400:1047–60. - PubMed
-
- Fang L, Lyu Z, Ai S, Du S, Zhou W, Zeng S, et al. Is cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia more cost-effective? new-perspective on economic evaluations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep. 2024;47:zsae122. - PubMed
-
- Hillman D, Mitchell S, Streatfeild J, Burns C, Bruck D, Pezzullo L. The economic cost of inadequate sleep. Sleep 2018;41. 10.1093/sleep/zsy083. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

