Caspases as master regulators of programmed cell death: apoptosis, pyroptosis and beyond
- PMID: 40555741
- PMCID: PMC12229594
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-025-01470-9
Caspases as master regulators of programmed cell death: apoptosis, pyroptosis and beyond
Abstract
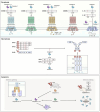
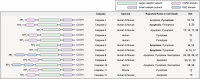
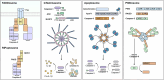
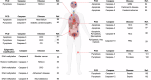
Caspases are crucial regulators of programmed cell death, mediating pathways such as apoptosis, pyroptosis, necroptosis and ferroptosis. Their activity is intricately controlled by epigenetic modifications, molecular interactions and post-translational changes, reflecting their central role in cellular homeostasis and disease mechanisms. Dysregulated caspase functions are linked to a wide array of conditions, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders and inflammatory diseases, establishing their importance as potential therapeutic targets. The roles and regulation of caspases across subcellular compartments and their molecular interactions provide critical insights into the complexity of programmed cell death. Here, this review synthesizes current knowledge on the diverse functions of caspases, offering a comprehensive foundation for exploring innovative therapeutic strategies.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Review on Caspases: Key Regulators of Biological Activities and Apoptosis.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Oct;60(10):5805-5837. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03433-5. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37349620 Review.
-
ZBP1 and TAK1: Master Regulators of NLRP3 Inflammasome/Pyroptosis, Apoptosis, and Necroptosis (PAN-optosis).Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019 Nov 26;9:406. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2019.00406. eCollection 2019. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 31850239 Free PMC article. Review.
-
S-acylation in apoptotic and non-apoptotic cell death: a central regulator of membrane dynamics and protein function.Biochem Soc Trans. 2025 Apr 29;53(2):487-96. doi: 10.1042/BST20253012. Biochem Soc Trans. 2025. PMID: 40304073 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Programmed cell death in paramyxovirus infection].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025 May 25;54(3):399-410. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2024-0512. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2025. PMID: 40394914 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
Regulation of Different Types of Cell Death by Noncoding RNAs: Molecular Insights and Therapeutic Implications.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025 Apr 30;8(5):1205-1226. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.4c00681. eCollection 2025 May 9. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2025. PMID: 40370994 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

