Exploring the m5C epitranscriptome of mRNAs in breast cancer cells through genome engineering and long-read sequencing approaches
- PMID: 40555775
- PMCID: PMC12187793
- DOI: 10.1007/s10142-025-01648-4
Exploring the m5C epitranscriptome of mRNAs in breast cancer cells through genome engineering and long-read sequencing approaches
Abstract
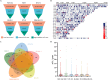
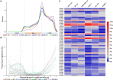
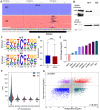
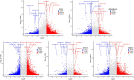
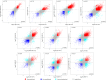
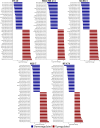
Epitranscriptomics has emerged as a rapidly evolving field that focused on studying post-transcriptional RNA modifications and their role in spatiotemporal regulation of gene expression. N6-methyladenosine (m6A) and 5-methylcytosine (m5C) represent the most extensively studied modifications on mRNAs. These reversible modifications, mediated by 'writer,' 'eraser,' and 'reader' proteins, dynamically fine-tune mRNA stability, splicing, and translation. Growing evidence links their dysregulation to pathological states, including cancer progression and metastasis, where their aberrant deposition on oncogenes or tumor suppressors alters cellular signaling and therapeutic responses. In the current study, we present a detailed analysis of the m5C epitranscriptomic landscape across distinct breast cancer molecular subtypes. Using CRISPR/Cas9, we confirm NSUN2 as a key m5C writer in human mRNAs. NSUN2 loss was validated by targeted sequencing and Western blotting. Furthermore, we demonstrate the regulatory effects of NSUN2 on its canonical mRNA targets, revealing its critical role in maintaining proper gene expression networks. Our findings strongly suggest that additional m5C writers contribute to m5C methylation machinery. Additionally, we assessed the functional impact of NSUN2 depletion on mRNAs harboring m5C sites using mRNA stability assays. Furthermore, our analysis revealed distinct m5C methylation patterns among breast cancer subtypes, highlighting unique m5C signatures associated with the disease. Notably, we identified specific hypomethylated and hypermethylated m5C sites in each breast cancer cell line, representing a universal m5C methylation signature for breast cancer. Our study constitutes the first comprehensive m5C epitranscriptomic atlas in human breast cancer and paves the way for future research aimed at developing targeted therapeutic interventions that leverage the m5C methylation landscape.
Keywords: 5-methylcytosine; Breast cancer; Epitranscriptomics; Gene expression; Nanopore sequencing; Post-transcriptional regulation; RNA biology; mRNA modifications.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: Not applicable. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests. Clinical trial number: Not applicable.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NSUN2/YBX1 promotes the progression of breast cancer by enhancing HGH1 mRNA stability through m5C methylation.Breast Cancer Res. 2024 Jun 6;26(1):94. doi: 10.1186/s13058-024-01847-0. Breast Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38844963 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated Nanopore and short-read RNA sequencing identifies dysregulation of METTL3- m6A modifications in endocrine therapy- sensitive and resistant breast cancer cells.Funct Integr Genomics. 2025 Jul 9;25(1):149. doi: 10.1007/s10142-025-01658-2. Funct Integr Genomics. 2025. PMID: 40632306 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering the Epitranscriptome: A Review on mRNA Modifications and Emerging Frontiers.Genes (Basel). 2025 Aug 12;16(8):951. doi: 10.3390/genes16080951. Genes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40870000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanopore direct RNA sequencing of human transcriptomes reveals the complexity of mRNA modifications and crosstalk between regulatory features.Cell Genom. 2025 Jun 11;5(6):100872. doi: 10.1016/j.xgen.2025.100872. Epub 2025 May 12. Cell Genom. 2025. PMID: 40359935 Free PMC article.
-
The role of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) RNA methylation modification in kidney diseases: from mechanism to therapeutic potential.PeerJ. 2025 Aug 27;13:e19940. doi: 10.7717/peerj.19940. eCollection 2025. PeerJ. 2025. PMID: 40895041 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acera Mateos P, Ravindran AJS, Srivastava A, Woodward A, Mahmud K, Kanchi S, Guarnacci M, Xu M, Z J, Zhou WSY, Sneddon Y, Hamilton A, Gao W, Hayashi JLMS, Wickramasinghe R, Zarnack V, Preiss K, Burgio T, Dehorter G, Eyras NNES E (2024) Prediction of m6A and m5C at single-molecule resolution reveals a transcriptome-wide co-occurrence of RNA modifications. Nat Commun 15:3899. 10.1038/s41467-024-47953-7 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen YS, Yang WL, Zhao YL, Yang YG (2021) Dynamic transcriptomic m(5) C and its regulatory role in RNA processing. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA 12:e1639. 10.1002/wrna.1639 - PubMed
-
- Cui Y, Lv P, Zhang C (2024) NSUN6 mediates 5-methylcytosine modification of METTL3 and promotes colon adenocarcinoma progression. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 38:e23749. 10.1002/jbt.23749 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

