Total thyroidectomy performed under general anesthesia with venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during a thyroid storm: a case report
- PMID: 40556009
- PMCID: PMC12188653
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-025-03491-x
Total thyroidectomy performed under general anesthesia with venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation during a thyroid storm: a case report
Abstract
Background: Thyroid storm (TS) is an endocrine emergency requiring aggressive medical management. In severe cases, hemodynamic instability may necessitate extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) support as a bridge to definitive surgical treatment. ECMO is categorized into two types: venoarterial (V-A) ECMO, which provides both cardiac and pulmonary support, and venovenous (V-V) ECMO, which supports only pulmonary function. Surgery is generally not recommended for patients with unstable TS due to the high risk of complications, even when ECMO support is in place. Here, we present a case of a 44-year-old man initially improved with V-A ECMO for TS with cardiogenic shock, but later developed refractory hypoxemia due to pulmonary thromboembolism (PTE). He subsequently underwent emergency thyroidectomy with continuous support from V-V ECMO.
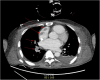
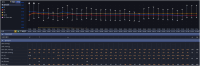
Case presentation: A 44-year-old man presented to our hospital with complaints of palpitations. He had a recent history of coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) infection, which may have exacerbated undiagnosed hyperthyroidism, leading to thyroid storm and cardiogenic shock (left ventricular ejection fraction [LVEF], 13%). Heart failure improved with immediate medical management and V-A ECMO for 4 days, resulting in LVEF, 30%. V-A ECMO provide both respiratory and cardiac support, allowing myocardial recovery. Although the patient's cardiac output improved, uncontrolled tachycardia persisted. Medical treatment for hyperthyroidism-associated tachycardia was continued after V-A ECMO weaning but failed to achieve adequate rate control. Ten days after weaning V-A ECMO, the patient suddenly developed pulmonary thromboembolism and hypoxia despite ongoing heparinization. To manage refractory hypoxia, V-V ECMO was initiated, as it exclusively provides respiratory support. Given that persistent TS was the underlying cause of the patient's instability, we proceeded with thyroidectomy under general anesthesia with V-V ECMO support, despite the associated risks. On postoperative day 4, the patient was successfully weaned off V-V ECMO. By postoperative day 18, he was discharged without complications, with an improved LVEF of 52.5%.
Conclusions: This is the first reported case of total thyroidectomy performed while on V-V ECMO support for TS complicated by PTE. Although V-V ECMO is more susceptible to hemodynamic instability than V-A ECMO, this case demonstrates that thyroidectomy can be successfully performed with appropriate anesthesia management. Additionally, careful selection of the ECMO modality based on the patient's condition is crucial for optimal management.
Keywords: COVID-19; Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; General anesthesia; Thyroid crisis; Thyroidectomy.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations. Ethics approval and consent to participate: It was approved by the Chonnam National University Hospital Institutional Review Board. (CNUH-EXP-2022–306). Consent for publication: Written HIPAA consent using our institutional form was obtained from the patient for the publication of this case report. Competing interests: The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Galindo RJ, Hurtado CR, Pasquel FJ, García Tome R, Peng L, Umpierrez GE. National Trends in Incidence, Mortality, and Clinical Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized for Thyrotoxicosis With and Without Thyroid Storm in the United States, 2004–2013. Thyroid : official journal of the American Thyroid Association. 2019;29(1):36–43. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ross DS, Burch HB, Cooper DS, Greenlee MC, Laurberg P, Maia AL, Rivkees SA, Samuels M, Sosa JA, Stan MN, et al. 2016 American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis. Thyroid : official journal of the American Thyroid Association. 2016;26(10):1343–421. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Voll M, Øystese KA, Høiskar E, Johansen O, Nyvold C, Norheim I, von Lueder TG, Andersen G. Case report: a patient with thyroid storm, refractory cardiogenic shock, and cardiac arrest treated with Lugol’s iodine solution and veno-arterial extra corporal membrane oxygenation support. European heart journal Case reports. 2021;5(2):ytab017. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

