Targeted Delivery of Lidocaine in Breast Cancer Cells via Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Nanoparticles
- PMID: 40556462
- PMCID: PMC12388163
- DOI: 10.1002/cphc.202401128
Targeted Delivery of Lidocaine in Breast Cancer Cells via Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 Nanoparticles
Abstract
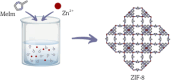
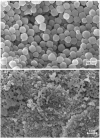
The aim of this article is to use zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) as drug delivery system for lidocaine, a local anesthetic with recently discovered antitumoral effects, in particular for the early-stage treatment of breast cancer. A previously optimized ZIF-8 synthetic method is employed, and the prepared material is deeply characterized with X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), surface area analysis, scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). After confirming the successful synthetic outcomes, a tailored loading procedure is developed to incorporate lidocaine within the ZIF-8 pores. The effectiveness of this loading process is verified using UV-Vis spectroscopy and TGA, while SEM and attenuated total reflectance-mid infrared spectroscopy further confirms the presence of lidocaine within the MOF pores. Afterwards, the pH-responsive drug release by dialyzing the lidocaine@ZIF-8 sample is tested either at physiological or at weakly acid pH values by UV spectroscopy on the dialysis solutions. Finally, the MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells viability of lidocaine@ZIF-8 system is tested and compared with the free drug and the MOF alone, confirming its significant capabilities in the reduction of cells viability.
Keywords: ZIF‐8 nanoparticles; anticancer application; lidocaine; pH‐regulated delivery; targeted delivery.
© 2025 The Authors. ChemPhysChem published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Furukawa H., Cordova K. E., O’Keeffe M., Yaghi O. M., Science 2013, 341, 974. - PubMed
-
- Freund R., Zaremba O., Dinca M., Arnauts G., Ameloot R., Skorupskii G., Bavykina A., Gascon J., Ejsmont A., Goscianska J., Kalmutzki M., Lächelt U., Ploetz E., Diercks C.S., Wuttke S., Angew. Chem. Int. Edit. 2021, 60, 23975. - PubMed
-
- García‐García P., Müller M., Corma A., Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 2979.
-
- Moharramnejad M., Ehsani A., Shahi M., Gharanli S., Saremi H., Malekshah R. E., Basmenj Z. S., Salmani S., Mohammadi M., J. Drug Delivery Sci. Technol. 2023, 81, 104285.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

