Diagnostic yield of intraoperative frozen sections obtained through robot-assisted stereotactic biopsy of brain lesions
- PMID: 40556650
- PMCID: PMC12185993
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1544613
Diagnostic yield of intraoperative frozen sections obtained through robot-assisted stereotactic biopsy of brain lesions
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the diagnostic yield and diagnostic accuracy of intraoperative frozen sections obtained through robot-assisted stereotactic biopsy of brain lesions.
Methods: The medical records of 87 patients who underwent 89 robot-assisted stereotactic biopsies of brain lesions at our institution between June 2015 and January 2024 were retrospectively reviewed. All patients were assessed using hematoxylin/eosin (HE) staining of intraoperative frozen sections, and intraoperative immunohistochemical examination when necessary. A final diagnosis derived from integrated diagnostics (neoplastic diseases) or final histopathologic examination (non-neoplastic diseases) was the 'gold standard'. Intraoperative frozen section results were divided into 3 categories: confirmed diagnosis, tentative diagnosis, and misdiagnosis. Subgroup analyses of negative intraoperative frozen section results, tentative diagnoses or misdiagnoses were conducted stratified by lesion size and lesion type.
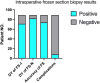
Results: Mean turn-around time for intraoperative frozen sections was 26 ± 5.6 min (range, 20-62 min). 1 (FS-1) to 4 (FS-N) (median, 1) intraoperative frozen sections were evaluated per patient. There was a significant increase in positive results from FS-1 (79.77%; n = 71/89) to FS-N (92.13%; n = 82/89) (p = 0.018). FS-1 results were negative in 18 (20.22%) patients. Among these, FS-N results were positive after adjusting the puncture depth or changing the target in 11 patients. The overall concordance rate of intraoperative frozen section to final diagnosis was 91.1% (confirmed diagnosis, n = 73; tentative diagnosis, n = 8). Intraoperative immunohistochemistry was performed on the frozen sections of 38 patients (42.7%). Among the patients with negative FS-1 results, tentative diagnoses or misdiagnoses, there were 12, 6 and 7 patients with medium sized lesions, respectively. Eight patients with negative FS-1 results had high-grade glioma.
Conclusion: The diagnostic yield of intraoperative frozen sections obtained through robot-assisted stereotactic biopsy of brain lesions is high. If the first frozen section result is negative, additional specimens should be obtained after adjusting the puncture depth or the target. Lesions that are difficult to distinguish morphologically on HE staining may be examined using intraoperative immunohistochemistry. High-grade glioma may be more prone to tentative or misdiagnosis due to heterogeneity of the lesion.
Keywords: brain tumor; diagnostic yield; frozen section; robotics; stereotactic biopsy.
Copyright © 2025 Chen, Luo, Lin, Deng, Zhang, Zeng, Lin and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Colombet M, Bray F. Cancer incidence in five continents, CI5plus: IARC CancerBase No. 9. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; (2018).
-
- Zanello M, Roux A, Senova S, Peeters S, Edjlali M, Tauziede-Espariat A, et al. Robot-assisted stereotactic biopsies in 377 consecutive adult patients with Supratentorial diffuse gliomas: diagnostic yield, safety, and postoperative outcomes. World Neurosurg. (2021) 148:e301–13. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2020.12.127, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

