Proton beam therapy for a patient with prostatic rhabdomyosarcoma: a case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 40556677
- PMCID: PMC12185390
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1490098
Proton beam therapy for a patient with prostatic rhabdomyosarcoma: a case report and review of the literature
Abstract
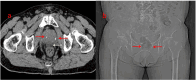
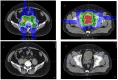
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a malignant tumor that is more common in children and rarely occurs in adults. Its prognosis mainly depends on the tumor stage and genetic type. In the past few decades, the survival rate of rhabdomyosarcoma has been significantly improved. Embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (ERMS), alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (ARMS), and pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma (PRMS) are common types of rhabdomyosarcoma. ERMS and ARMS are more common in children, while PRMS is more common in adults and has a poor prognosis. We report a case of a 40-year-old patient with ARMS. His chief complaint was difficulty urinating. The diagnosis was confirmed by puncture biopsy of the prostate, and pelvic lymph node metastasis was already present at the time of diagnosis. The patient underwent seven courses of chemotherapy and proton therapy and five courses of adjuvant chemotherapy. Unfortunately, 8 months after proton beam therapy, the patient showed disease progression (bone metastasis). This case illustrates the difficulties in managing late-stage prostatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma and is the first case reported in our hospital to be treated with proton beam therapy in an adult with ARMS of the prostate.
Keywords: alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma; chemotherapy; prostate; proton beam therapy; rhabdomyosarcoma.
Copyright © 2025 Yang, Mizoe, Komaki and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

