The current status, trends, and challenges of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias in Asia (1990-2036)
- PMID: 40556904
- PMCID: PMC12185285
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1583339
The current status, trends, and challenges of Alzheimer's disease and other dementias in Asia (1990-2036)
Abstract
Background: With global aging, Alzheimer's disease (AD) and other dementias have emerged as significant health threats to the older adults, garnering considerable attention due to their impact on public health. Despite the substantial burden of dementia in Asia, targeted research remains limited. This study aims to assess the current burden, future trends, risk factors, and inequalities in Asia.
Method: The GBD 2021 study was utilized to evaluate the numbers and age-standardized rates (ASRs) of prevalence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life-years (DALYs) of AD and other dementias from 1990 to 2021. Joinpoint regression analysis was performed to assess the trends during this period, while the Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) model was employed to predict future trends. Additionally, the relationship between disease burden and sociodemographic index (SDI) was also analyzed.
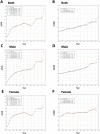
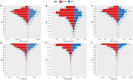
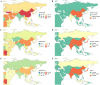
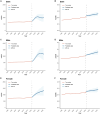
Results: In 2021, Asia experienced a 250.44% increase in prevalent cases, a 297.34% rise in mortality, and a 249.54% surge in DALYs for AD and other dementias compared to 1990. Meanwhile, the age-standardized prevalence rate, age-standardized mortality rate, and age-standardized DALY rate also exhibited varying degrees of rise from 1990 to 2021. Demographically, the disease burden was higher in women and those aged 65 and above. Regionally, the burden was highest in East Asia and relatively low in South and Central Asia. Nationally, China, India, Japan, and Indonesia reported the most cases. Over the next 15 years, the age-standardized prevalence rate in Asia is expected to peak in 2028 before declining, while the age-standardized mortality rate is anticipated to keep rising. An overall "V" shaped association was found between sociodemographic index (SDI) and the age-standardized DALY rate in Asia. Only smoking, high fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and high BMI were identified as causal risk factors within the GBD framework.
Conclusion: The burden of AD and other dementias in Asia has significantly increased over the past three decades and is expected to persistently impact Asian populations, particularly in developing countries experiencing rapid demographic shifts. Women and the older adult should be a focus of attention. It is imperative to implement targeted prevention and intervention strategies, enhance chronic disease management, and control risk factors.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease and other dementia; disability-adjusted life years; global burden of disease; mortality; prevalence; risk factors.
Copyright © 2025 He, Zhang, Hu, Qiao, Yin, Li, Lin, Wu, Qin, Law, Hu and Yu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The disease burden, risk factors and future predictions of Alzheimer's disease and other types of dementia in Asia from 1990 to 2021.J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025 May;12(5):100122. doi: 10.1016/j.tjpad.2025.100122. Epub 2025 Mar 7. J Prev Alzheimers Dis. 2025. PMID: 40057462 Free PMC article.
-
Global burden trends and future predictions of ischemic heart disease attributable to air pollution in people aged 60 years and older, 1990-2021.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 4;13:1598092. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1598092. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40687134 Free PMC article.
-
Trend analysis and future predictions of global burden of alzheimer's disease and other dementias: a study based on the global burden of disease database from 1990 to 2021.BMC Med. 2025 Jul 1;23(1):378. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-04169-w. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40597083 Free PMC article.
-
CSF tau and the CSF tau/ABeta ratio for the diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease dementia and other dementias in people with mild cognitive impairment (MCI).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Mar 22;3(3):CD010803. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010803.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28328043 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

