Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Versus Anti-Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in PD-L1-Negative Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 40556968
- PMCID: PMC12185128
- DOI: 10.14740/wjon2520
Anti-Programmed Cell Death-1 Versus Anti-Programmed Death-Ligand 1 (PD-L1) in PD-L1-Negative Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) which target programmed cell death-1 (PD-1) receptor or its ligand (PD-L1) are used extensively in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). In this article, we compared the relative efficacy of PD-1 inhibitors and PD-L1 inhibitors in PD-L1-negative advanced NSCLC.
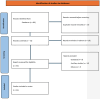
Methods: We searched MEDLINE (host: PubMed, Scopus, and Google Scholar) for randomized trials for advanced NSCLC in which ICIs (anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1) were used where outcome data were reported based on PD-L1 testing, including the subset of PD-L1-negative patients. We extracted hazard ratios (HRs) and related 95% confidence intervals (CIs) and/or P values for progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) for the PD-L1-negative subgroup of each included trial. We then pooled data using a random effects meta-analysis and compared anti-PD-1 to anti-PD-L1 inhibitors. Variations in effect size were examined using subgroup analyses.
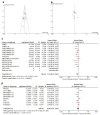
Results: Twenty-three trials were included in the meta-analysis. PD-L1 testing was performed in all participants. A total of 4,548 PD-L1-negative patients were included in the analysis, representing 33% of all participants in the included clinical trials. Overall, the addition of anti-PD-1 was associated with better OS in PD-L1-negative advanced NSCLC patients (HR: 0.75, 95% CI: 0.67 - 0.83, P < 0.01), while the addition of anti-PD-L1 inhibitors showed no improvement in OS (HR: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.78 - 1.05, P = 0.18). Compared to anti-PD-L1 agents, anti-PD-1 resulted in better OS in PD-L1-negative patients (HR: 0.83, 95% CI: 0.67 - 0.99, P = 0.01). The differential benefit of anti-PD-1 over anti-PD-L1 was of larger magnitude when checkpoint inhibitors were used in the first-line setting (pairwise comparison HR: 0.79, 95% CI: 0.66 - 0.93, P = 0.01), while there was no difference for later lines of therapy (pairwise comparison 1.13; 95% CI: 0.82 - 1.55, P = 0.45). These differences in OS were not observed when pooling PFS data.
Conclusions: Compared to checkpoint inhibitors targeting PD-L1, those targeting PD-1 are associated with better OS in PD-L1-negative advanced NSCLC, a finding influenced by trials performed in the first-line sitting. These data should be validated using real-world studies.
Keywords: Anti-PD-1; Anti-PD-L1; Immunotherapy; Non-small cell lung cancer; PD-L1 negative.
Copyright 2025 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Laith Al-Showbaki: consulting from Novartis, AstraZeneca, and Janssen. Eitan Amir: consulting from Gilead and Novartis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparison of efficacy and safety of PD-1/PD-L1 combination therapy in first-line treatment of advanced NSCLC: an updated systematic review and network meta-analysis.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Oct;26(10):2488-2502. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03442-3. Epub 2024 Apr 16. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38625495
-
Targeted therapy for advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase (<I>ALK</I>)-rearranged non-small cell lung cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Jan 7;1(1):CD013453. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013453.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 34994987 Free PMC article.
-
Nivolumab for adults with Hodgkin's lymphoma (a rapid review using the software RobotReviewer).Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jul 12;7(7):CD012556. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012556.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30001476 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of immune checkpoint inhibitors for advanced non-small cell lung cancer with or without PD-L1 selection: A systematic review and network meta-analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2023 Sep 20;136(18):2156-2165. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000002750. Epub 2023 Aug 18. Chin Med J (Engl). 2023. PMID: 37596898 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of Efficacy and Safety of Single and Double Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Based First-Line Treatments for Advanced Driver-Gene Wild-Type Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis.Front Immunol. 2021 Aug 16;12:731546. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731546. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34484242 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
