Ameliorative effect of citicoline on cyclophosphamide-induced lung injury
- PMID: 40557095
- PMCID: PMC12184473
- DOI: 10.5455/OVJ.2025.v15.i5.39
Ameliorative effect of citicoline on cyclophosphamide-induced lung injury
Abstract
Background: Cyclophosphamide (CP) is known to cause pulmonary injury through free radical production and proinflammatory cytokines activation. Lung damage is associated with significant mortality, primarily due to the development of severe inflammation and pulmonary edema. On the other hand, citicoline, a key intermediate in the phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis pathway, has neurovascular protective and reparative properties. Numerous studies have highlighted the potential antioxidant and antiinflammatory effects of this agent in the context of various pathological conditions.
Aim: Our study aimed to explore the potential protective effects of citicoline against oxidative stress, inflammation, and tissue damage caused by CP in an experimental model.
Methods: Rats were given 200 mg/kg of CP as a single dose, either alone or in combination with citicoline (500 or 250 mg/kg), administered orally once daily for 14 days, beginning 7 days prior to CP administration. On the final day of the experiment, all animals were euthanized, and lung tissues were collected for further analysis.
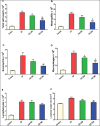
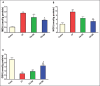
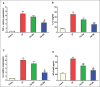
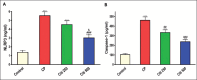
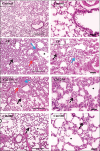
Results: CP administration led to a significant elevation in the lung-to-body weight ratio, inflammatory cell infiltration, and elevated levels of lactate dehydrogenase, total protein, nuclear factor kappa B, Interleukin-1β, NOD-like receptor protein 3, and caspase-1 in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid. Furthermore, CP treatment increased the concentrations of malondialdehyde and nitrate/nitrite and reduced glutathione levels in the lungs. Additionally, mRNA of Interleukin 6 and tumor necrosis factor-α levels were significantly elevated. These biochemical alterations were corroborated by histopathological findings, which revealed significant lung tissue damage. However, treatment with citicoline significantly reduced the pulmonary pathological changes induced by CP.
Conclusion: These findings imply that citicoline's antiinflammatory and antioxidant properties provide protection against CP-induced lung damage.
Keywords: Citicoline; Cyclophosphamide; Lung injury; NF-kB; NLRP-3.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicting interests.
Figures

References
-
- Abdel-Aziz N., Moustafa E.M., Saada H.N. The impact of citicoline on brain injury in rats subjected to head irradiation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2021;28(8):9742–9752. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Aziz N., Saif-Elnasr M. Citicoline modulates inflammatory signaling pathways in the spleen of rats exposed to gamma-radiation. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2024;46(4):564–571. - PubMed
-
- Abdel-Salam O., Youness E., Mohamed N., El-Moneim O., Shaffie N. Citicoline protects against tramadol-induced oxidative stress and organ damage. React. Oxyg. Species. 2019;7(20):106–120.
-
- Adibhatla R.M., Hatcher J.F. Citicoline decreases phospholipase A2 stimulation and hydroxyl radical generation in transient cerebral ischemia. J. Neurosci. Res. 2003;73(3):308–315. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
