Nanoparticle approaches for manipulating cytokine delivery and neutralization
- PMID: 40557148
- PMCID: PMC12185478
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1592795
Nanoparticle approaches for manipulating cytokine delivery and neutralization
Abstract
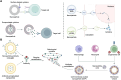
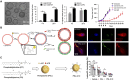
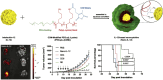
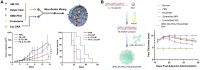
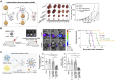
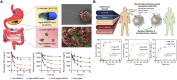
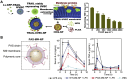
Cytokines are crucial regulators of inflammation and immune tolerance, making them promising targets for treating immune-related diseases like cancer, infections, and autoimmune disorders. While cytokine-based therapies have shown potential, challenges such as dose-limiting toxicity and suboptimal pharmacokinetics have constrained their clinical success. Recent advancements in nanotechnology offer innovative solutions to these limitations, particularly through the use of nanoparticle-based platforms that enhance cytokine delivery and neutralization. This review begins by examining the landscape of cytokine delivery, emphasizing how it can be accomplished using nanoparticle systems encapsulating proteins, DNA or mRNA payloads. We then discuss recent progress on platforms for nanoparticle-based cytokine neutralization, including nanoparticle-antibody complexes and cell membrane-coated nanoparticles. Finally, we highlight the latest clinical developments in cytokine-based therapies employing these strategies before addressing the critical challenges ahead that need to be overcome in order to fully realize the therapeutic potential of nanoparticle-based cytokine manipulation.
Keywords: autoimmune disease; biodetoxification; biomimetic nanoparticle; cytokine delivery; cytokine neutralization; nanodelivery.
Copyright © 2025 Wang, Kubiatowicz, Zhang, Bao, Fang and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
How lived experiences of illness trajectories, burdens of treatment, and social inequalities shape service user and caregiver participation in health and social care: a theory-informed qualitative evidence synthesis.Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025 Jun;13(24):1-120. doi: 10.3310/HGTQ8159. Health Soc Care Deliv Res. 2025. PMID: 40548558
-
The use of Open Dialogue in Trauma Informed Care services for mental health consumers and their family networks: A scoping review.J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024 Aug;31(4):681-698. doi: 10.1111/jpm.13023. Epub 2024 Jan 17. J Psychiatr Ment Health Nurs. 2024. PMID: 38230967
-
Challenges in Exploiting Human H Ferritin Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Navigating Physiological Constraints.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024 Nov-Dec;16(6):e2016. doi: 10.1002/wnan.2016. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39541599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing the comparative effects of interventions in COPD: a tutorial on network meta-analysis for clinicians.Respir Res. 2024 Dec 21;25(1):438. doi: 10.1186/s12931-024-03056-x. Respir Res. 2024. PMID: 39709425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

