Advances in Functionalized Nanoparticles for Osteoporosis Treatment
- PMID: 40557247
- PMCID: PMC12186752
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S519945
Advances in Functionalized Nanoparticles for Osteoporosis Treatment
Abstract
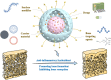
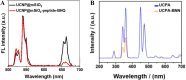
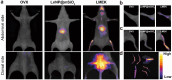
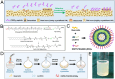
Osteoporosis (OP) represents a significant global health burden, characterized by reduced bone density and an increased risk of fractures due to imbalances in bone remodeling processes. Traditional therapeutic strategies, while mitigating symptoms, often lack the precision to address the multifactorial nature of OP effectively. In recent years, functionalized nanoparticles have emerged as a versatile platform, offering enhanced drug delivery, targeted therapy, and the potential for theranostic applications in OP treatment. This review examines the various types and architectures of functionalized nanoparticles, emphasizing their unique capabilities in targeting bone tissue and modulating bone metabolism. By focusing on their roles in inflammation modulation, oxidative stress reduction, and promoting bone regeneration, we discuss the mechanisms by which these nanoparticles offer multifunctional, synergistic effects. Additionally, we address the challenges in achieving controlled drug release, biocompatibility, and effective bone tissue penetration, proposing future directions that integrate emerging nanotechnologies, biomechanics, and regenerative medicine approaches to optimize therapeutic outcomes. This comprehensive review provides a foundation for the future development of functionalized nanoparticle therapies, positioning them as promising tools for advanced, personalized OP treatment.
Keywords: bone tissue targeting; drug delivery; functionalized nanoparticles; osteoporosis.
© 2025 Cai et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Extracellular Vesicle-Integrated Biomaterials in Bone Tissue Engineering Applications: Current Progress and Future Perspectives.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 17;20:7653-7683. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S522198. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40546799 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanistic insight into nanomedicine for polycystic ovary syndrome.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jun 21;52(1):618. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10709-7. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40544202 Review.
-
Stepwise Administration of Bone-Targeted Lipid Nanoparticles Encapsulating Valproic Acid and TUDCA Facilitates In Vivo Direct Reprogramming for Osteoporosis Treatment.Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025 Aug;22(6):831-845. doi: 10.1007/s13770-025-00738-5. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2025. PMID: 40553371
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Nanomedicine-Driven Approaches for Kartogenin Delivery: Advancing Chondrogenic Differentiation and Cartilage Regeneration in Tissue Engineering.Int J Nanomedicine. 2025 Jun 13;20:7443-7468. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S525580. eCollection 2025. Int J Nanomedicine. 2025. PMID: 40535835 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brent MB. Pharmaceutical treatment of bone loss: from animal models and drug development to future treatment strategies. Pharmacol Ther. 2023;244:108383. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

