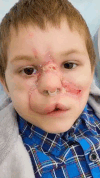
First Russian Experience of Pediatric Subtotal Facial Tissue Replantation
- PMID: 40557301
- PMCID: PMC12187312
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000006906
First Russian Experience of Pediatric Subtotal Facial Tissue Replantation
Abstract
Treatment and rehabilitation of patients with posttraumatic, contaminated, lacerated wounds present a complex challenge. The concept of delayed, multistage treatment, as well as the rehabilitation protocols for pediatric patients is associated with a series of reconstructive procedures, one of which is face transplantation; however, it remains an unresolved issue to date due to the development of immunologic tissue intolerance by the recipient, as well as various psychosocial rehabilitation challenges. The challenge of successful pediatric replantation creates interest in the global medical community to develop generalized algorithms for managing patients with posttraumatic subtotal facial defects. This case report demonstrated the experience of the first posttraumatic subtotal facial replantation less than 12 hours after injury in a pediatric patient in Russia. The goal of this work was to show the algorithm used in the case of a pediatric posttraumatic subtotal facial defect in hopes of aiding the future development of such guidelines.
Copyright © 2025 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial interest to declare in relation to the content of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Tu AH, Girotto JA, Singh N, et al. Facial fractures from dog bite injuries. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;109:1259–1265. - PubMed
-
- Verbo EV, Butsan SB, Brusova LA, et al. Balance techniques of plastic defect correction in reconstruction of the middle facial zone. Ann Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2016;1:67–68.
-
- Godfrey ND, Akyurek M. Microvascular replantation of the avulsed lip. J Craniofac Surg. 2018;29:e717–e720. - PubMed
-
- Dikarev A, Porhanov V, Kochergina E, et al. Translocation composite facial flap as approach for surgical treatment of tumors of the paranasal sinuses and skull base. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;44:e54.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources