Semi-supervised Segmentation of Histopathology Images with Noise-Aware Topological Consistency
- PMID: 40557360
- PMCID: PMC12185923
- DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-73229-4_16
Semi-supervised Segmentation of Histopathology Images with Noise-Aware Topological Consistency
Abstract
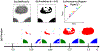
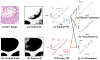
In digital pathology, segmenting densely distributed objects like glands and nuclei is crucial for downstream analysis. Since detailed pixel-wise annotations are very time-consuming, we need semi-supervised segmentation methods that can learn from unlabeled images. Existing semi-supervised methods are often prone to topological errors, e.g., missing or incorrectly merged/separated glands or nuclei. To address this issue, we propose TopoSemiSeg, the first semi-supervised method that learns the topological representation from unlabeled histopathology images. The major challenge is for unlabeled images; we only have predictions carrying noisy topology. To this end, we introduce a noise-aware topological consistency loss to align the representations of a teacher and a student model. By decomposing the topology of the prediction into signal topology and noisy topology, we ensure that the models learn the true topological signals and become robust to noise. Extensive experiments on public histopathology image datasets show the superiority of our method, especially on topology-aware evaluation metrics. Code is available at https://github.com/Melon-Xu/TopoSemiSeg.
Keywords: Histopathology Imaging; Semi-supervised Segmentation; Topological Consistency.
Figures
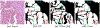
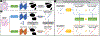
Similar articles
-
Boundary-Guided Contrastive Learning for Semi-Supervised Medical Image Segmentation.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025 Jul;44(7):2973-2988. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2025.3556482. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40168231
-
Semi-Supervised Learning Allows for Improved Segmentation With Reduced Annotations of Brain Metastases Using Multicenter MRI Data.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025 Jun;61(6):2469-2479. doi: 10.1002/jmri.29686. Epub 2025 Jan 10. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2025. PMID: 39792624 Free PMC article.
-
IHE-Net:Hidden feature discrepancy fusion and triple consistency training for semi-supervised medical image segmentation.Artif Intell Med. 2025 Oct;168:103229. doi: 10.1016/j.artmed.2025.103229. Epub 2025 Jul 31. Artif Intell Med. 2025. PMID: 40763409
-
Interventions to prevent occupational noise-induced hearing loss.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 7;7(7):CD006396. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD006396.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28685503 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hard Negative Sample Mining for Whole Slide Image Classification.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2024 Oct;15004:144-154. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-72083-3_14. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2024. PMID: 40556770 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basak H, Yin Z: Pseudo-label guided contrastive learning for semi-supervised medical image segmentation. In: CVPR; (2023)
-
- Berthelot D, Carlini N, Goodfellow I, Papernot N, Oliver A, Raffel CA: Mixmatch: A holistic approach to semi-supervised learning. In: NeurIPS; (2019)
-
- Cao H, Wang Y, Chen J, Jiang D, Zhang X, Tian Q, Wang M: Swin-unet: Unet-like pure transformer for medical image segmentation. In: ECCV; (2022)
-
- Chen G, Ru J, Zhou Y, Rekik I, Pan Z, Liu X, Lin Y, Lu B, Shi J: Mtans: Multi-scale mean teacher combined adversarial network with shape-aware embedding for semi-supervised brain lesion segmentation. NeuroImage (2021) - PubMed
-
- Chen LC, Zhu Y, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H: Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation. In: ECCV; (2018)
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
