Electrolyte Transport Parameters and Interfacial Effects in Calcium Metal Batteries: Analogies and Differences to Magnesium and Lithium Counterparts
- PMID: 40557607
- PMCID: PMC12412554
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202506498
Electrolyte Transport Parameters and Interfacial Effects in Calcium Metal Batteries: Analogies and Differences to Magnesium and Lithium Counterparts
Abstract
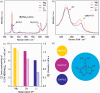
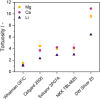
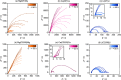
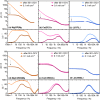
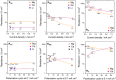
Magnesium and calcium metal batteries are promising emerging technologies. Their high capacity and low redox potential translate to a high theoretical energy density, making them attractive candidates for future energy storage solutions. Owing to their neighboring position and the diagonal relationship in the periodic table to lithium, Mg2+, Ca2+, and Li+ ions feature commonalities in terms of ionic radius, carried charge, and charge density. The present study aims to shed light on the similarities but also differences of Ca electrolytes and metal anodes in comparison to their Mg and Li counterparts in terms of transport properties and processes at the anode/electrolyte interface, respectively. To ensure comparability, an electrolyte comprising B(hfip)4 - anions in monoglyme is applied in either case. By executing galvanostatic polarization and pulsing with different separator materials, the separator tortuosity, diffusion coefficient, and transference number are determined. Further, the charge transfer characteristics as well as the adsorption layer and solid electrolyte interphase formation are investigated by electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The cation charge density was found to be crucial for diffusion and desolvation processes, yet surprisingly, also a cation-dependent separator tortuosity was observed. The study concludes with a recommendation on suitable separators for each metal battery system.
Keywords: EIS; electrolyte transport; metal anode battery; multivalent metals; separator tortuosity.
© 2025 The Author(s). Advanced Science published by Wiley‐VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Shannon R. D., Acta Crystallogr. A 1976, 32, 751.
-
- Mandai T., Naya H., Masu H., J. Phys. Chem. C 2023, 127, 7987.
-
- Singh R., Janakiraman S., Agrawal A., Nayak D., Ghosh S., Biswas K., Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 13677.
-
- Du W., Hao Z., Iacoviello F., Sheng L., Guan S., Zhang Z., Brett D. J. L., Wang F. R., Shearing P. R., Small Methods 2021, 5, 2001193. - PubMed
-
- Yu X., Manthiram A., ACS Energy Lett. 2016, 1, 431.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
