Hybridization capture sequencing for Vibrio spp. and associated virulence factors
- PMID: 40558084
- PMCID: PMC12345146
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.00516-25
Hybridization capture sequencing for Vibrio spp. and associated virulence factors
Abstract
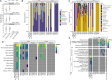
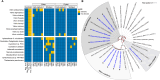
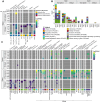
Proliferation of Vibrio spp. in aquatic ecosystems is associated with climate change and, concomitantly, increased incidence of vibriosis. They are autochthonous to aquatic environments globally, but traditional metagenomic methods for detecting and typing pathogenic Vibrio spp. are challenged by their presence in relatively low abundance and ability to persist in a viable but nonculturable state. In the study reported here, hybridization capture sequencing (HCS) was employed to profile low-abundance Vibrio spp. in environmental samples. The HCS panel targeted a family of molecular chaperones (CPN60) specific to 69 Vibrio spp. and 162 Vibrio-specific virulence factors. This approach was evaluated in parallel with traditional whole-community shotgun sequencing in a metagenomic analysis of water and oyster samples collected from the Chesapeake Bay. In addition, Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus strains isolated from the samples were subjected to whole-genome sequencing to determine the genetic characteristics of pathogenic Vibrio spp. circulating in an aquatic environment. HCS, employed to determine the incidence and characterization of specific Vibrio spp., yielded significantly greater metagenomic insight, notably a variety of other Vibrio spp., including detection of Vibrio cholerae, Vibrio fluvialis, and Vibrio aestuarianus, in addition to Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus, and also important virulence factors not detectable using traditional molecular methods. Thus, pathogenic Vibrio spp. in aquatic ecosystems may be far more common than currently understood. It is concluded that environmental surveillance should include HCS, a valuable tool for the detection and characterization of pathogenic agents in aquatic ecosystems, notably vibrios.IMPORTANCEThe increasing prevalence of pathogenic Vibrio spp. in aquatic ecosystems, driven by climate change, is closely linked to a rise in cholera and vibriosis cases, emphasizing the need for improved environmental surveillance. Vibrios are naturally occurring in aquatic environments globally, but traditional metagenomic methods for detecting and typing pathogenic Vibrio spp. are challenged by their presence in relatively low abundance and ability to persist in a viable but nonculturable state. In the study reported here, hybridization capture sequencing was employed to profile low-abundance Vibrio spp. in metagenomic samples, namely water and oysters collected from the Chesapeake Bay. This approach was evaluated in parallel with traditional whole-community shotgun sequencing and whole-genome sequencing of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and Vibrio vulnificus strains isolated from the samples. Results suggest pathogenic Vibrio spp. in aquatic ecosystems may be far more common than currently understood, when multiple methods are considered for environmental surveillance.
Keywords: Vibrio; hybridization capture; metagenomics; microbiome; next generation sequencing; targeted enrichment; virulence; whole-genome sequencing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

