Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins Targeting the L-HN Fragment of Tetanus Toxin Provided Protection In Vivo
- PMID: 40558102
- PMCID: PMC12189097
- DOI: 10.3390/antib14020048
Humanized VHH-hFc Fusion Proteins Targeting the L-HN Fragment of Tetanus Toxin Provided Protection In Vivo
Abstract
Background: Tetanus toxin, produced by Clostridium tetani, is the second deadliest known toxin. Antibodies capable of neutralizing tetanus toxin (TeNT) are vital for preventing and treating tetanus disease.
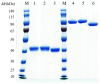
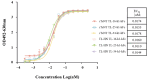
Methods: Herein, we screened thirty-six single variable domains on a heavy chain (VHHs) binding to the light chain (L) and the translocation domain (HN) (L-HN) fragment of TeNT from a phage-display library. Then, the L-HN-specific clones were identified, humanized, and fused with a human fragment crystallizable region (hFc) to form humanized VHH-hFc fusion proteins.
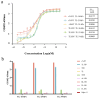
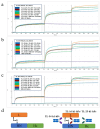
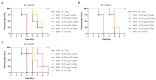
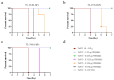
Results: The humanized VHH-hFc fusion proteins TL-16-h1-hFc, TL-25-h1-hFc, and TL-34-h1-hFc possessed potent efficacy with high binding affinity, specificity, and neutralizing activity. Only 0.3125 μg was required for TL-16-h1-hFc or TL-25-h1-hFc, and 0.625 μg was required for TL-34-h1-hFc to provide full protection against 10 × Lethal Dose 50 (LD50) TeNT. In the prophylactic setting, 125 μg/kg of TL-16-h1-hFc or TL-25-h1-hFc provided full protection even when they were injected 12 days before exposure to 10 × LD50 TeNT, while TL-34-h1-hFc was less effective. In the therapeutic setting, 25 μg/kg of TL-16-h1-hFc or TL-25-h1-hFc could provide complete protection when administered 24 h after exposure to 5 × LD50 TeNT, while TL-34-h1-hFc required 50 μg/kg.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that TL-16-h1-hFc, TL-25-h1-hFc, and TL-34-h1-hFc provide a bright future for the development of anti-TeNT preventive or therapeutic drugs.
Keywords: TL-HN; VHH; humanized VHH-hFc fusion protein; neutralization; phage-display library; tetanus toxin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

