Use of Daptomycin to Manage Severe MRSA Infections in Humans
- PMID: 40558207
- PMCID: PMC12190081
- DOI: 10.3390/antibiotics14060617
Use of Daptomycin to Manage Severe MRSA Infections in Humans
Abstract
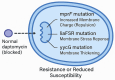
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) represents a major therapeutic challenge due to its multidrug-resistance and the associated clinical burden. Daptomycin (DAP), a cyclic lipopeptide antibiotic, has become a key agent for the treatment of severe MRSA infections owing to its rapid bactericidal activity and favourable safety profile. In this narrative review, we examine studies published between 2010 and April 2025. The data suggest that treatment with high-dose (8-10 mg kg⁻1) DAP shortened the time to blood-culture sterilisation by a median of 2 days compared with standard-dose vancomycin without increasing toxicity when model-informed area-under-the-curve monitoring was employed. Particular attention is given to the synergistic effects of DAP combined with fosfomycin or β-lactams, especially ceftaroline and ceftobiprole, in overcoming persistent and refractory MRSA infections; this approach results in a reduction in microbiological failure relative to monotherapy. Resistance remains uncommon (<2% of isolates), but recurrent mutations in mprF, liaFSR, and walK underscore the need for proactive genomic surveillance. Despite promising preclinical and clinical evidence supporting combination strategies, further randomized controlled trials are necessary to establish their definitive role in clinical practice, as are head-to-head cost-effectiveness evaluations. DAP remains a critical option in the evolving landscape of MRSA management, provided its use is integrated with precision dosing, resistance surveillance, and antimicrobial-stewardship frameworks.
Keywords: antibiotic resistance; bacteremia; combination therapy; daptomycin; methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Rybak M., Lomaestro B., Rotschafer J.C., Moellering R., Jr., Craig W., Billeter M., Dalovisio J.R., Levine D.P. Therapeutic monitoring of vancomycin in adult patients: A consensus review of the American Society of Health-System Pharmacists, the Infectious Diseases Society of America, and the Society of Infectious Diseases Pharmacists. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2009;66:82–98. doi: 10.2146/ajhp080434. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous