Where Do We Stand in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahead of EULAR/ACR 2025?
- PMID: 40558221
- PMCID: PMC12192006
- DOI: 10.3390/clinpract15060103
Where Do We Stand in the Management of Rheumatoid Arthritis Ahead of EULAR/ACR 2025?
Abstract
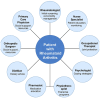
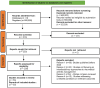
Background: Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterised by systemic inflammation and the progressive damage of joints, significantly impacting patients' quality of life. Managing this condition requires a complex approach that integrates pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies, alongside psychosocial support and patient education. Aim: This study aims to highlight the importance of an interdisciplinary approach in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, focusing on the role of pharmacological therapies, monitoring treatment response, and the involvement of a multidisciplinary team in the effective management of the disease. Methods: The analysis was based on a review of the specialised literature concerning the role of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs, both conventional and biological), the use of inflammatory markers (CRP and ESR), advanced imaging techniques, and the contribution of various medical specialities to the holistic management of rheumatoid arthritis. A total of 595,900 records were identified, of which 53 studies were ultimately included in the detailed analysis. Relevant studies from fields such as rheumatology, nutrition, psychology, and physical therapy were included. Results: The findings underline that DMARDs, in combination with other pharmacological therapies, remain essential for slowing disease progression. Monitoring treatment response through inflammatory markers and imaging techniques allows for the adjustment of therapeutic strategies and the prevention of complications. An interdisciplinary approach, involving the rheumatologist, general practitioner, physiotherapist, nutritionist, and psychologist, provides significant benefits, such as reducing inflammation, improving joint function, and offering psychosocial support. Conclusions: The effective management of rheumatoid arthritis requires a personalised interdisciplinary approach. Integrating various specialities, along with patient education and psychosocial support, contributes to better disease management, the prevention of disabilities, and improved quality of life. This review is not registered.
Keywords: DMARDs; NSAIDs; corticosteroids; imaging; inflammatory monitoring; interdisciplinary approach; personalised management; physical rehabilitation; psychosocial support; rheumatoid arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Poznyak A.V., Kirichenko T.V., Beloyartsev D.F., Churov A.V., Kovyanova T.I., Starodubtseva I.A., Sukhorukov V.N., Antonov S.A., Orekhov A.N. Rheumatoid Arthritis: What Inflammation Do We Face? J. Mol. Pathol. 2024;5:454–465. doi: 10.3390/jmp5040030. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous