Eleven-Year Incidence of Salivary Gland Tumors-A Retrospective, Single-Centered Study in Croatia
- PMID: 40558222
- PMCID: PMC12192542
- DOI: 10.3390/clinpract15060104
Eleven-Year Incidence of Salivary Gland Tumors-A Retrospective, Single-Centered Study in Croatia
Abstract
Background/objectives: The purpose of this study was to determine the incidence of salivary gland tumors based on age, gender, histological type, and localization over an eleven-year period at the University Hospital of Split.
Methods: The medical records of the Department of Otorhinolaryngology with Head and Neck Surgery and the Department of Maxillofacial Surgery at the University Hospital of Split regarding salivary gland tumors were searched from January 2012 to December 2022. The current fifth World Health Organization (WHO) Classification of Head and Neck Tumors and its criteria were considered during that process.
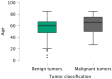
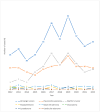
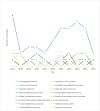
Results: Out of 404 patients, 211 (52.20%) were female and 193 (47.77%) male. The mean age was 60. There were four pediatric patients. Six patients had a combination of two different histological types of salivary gland tumors present simultaneously at the exact localization. Therefore, there were 410 histological types in total, 214 related to females and 196 to males. A total of 361 (88.05%) benign and 49 (11.95%) malignant primary salivary gland tumors were detected. The parotid gland was the predominant location (N = 361, 87.8%). There were no cases affecting the sublingual gland. Pleomorphic adenoma was the most common benign histological type (N = 169, 41.2%). The most common malignant histological types were adenoid cystic carcinoma (N = 9, 2.2%) and mucoepidermoid carcinoma (N = 9, 2.2%). The average incidences of salivary gland tumors in the 11 years for the four Dalmatian counties and the Republic of Croatia were 4.45/100,000 and 0.9/100,000, respectively.
Conclusions: The results of this study, primarily the ones concerning histological types and localization, do not deviate from general knowledge about salivary gland tumors. Simultaneous and ipsilateral occurrence of different histological types is a rare and extremely valuable finding. The average incidence for Dalmatian counties and the Republic of Croatia is within the range of the International Agency for Research on Cancer estimates.
Keywords: benign neoplasms; head and neck neoplasms; incidence; malignant neoplasms; salivary glands.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacological interventions for preventing dry mouth and salivary gland dysfunction following radiotherapy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017 Jul 31;7(7):CD012744. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012744. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2017. PMID: 28759701 Free PMC article.
-
Drugs for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults after general anaesthesia: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Oct 19;10(10):CD012859. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012859.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 33075160 Free PMC article.
-
Sertindole for schizophrenia.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005 Jul 20;2005(3):CD001715. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD001715.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2005. PMID: 16034864 Free PMC article.
-
Chemoprevention of colorectal cancer: systematic review and economic evaluation.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Jun;14(32):1-206. doi: 10.3310/hta14320. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20594533
-
Prophylactic mastectomy for the prevention of breast cancer.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004 Oct 18;(4):CD002748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002748.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2004. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010 Nov 10;(11):CD002748. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002748.pub3. PMID: 15495033 Updated.
References
-
- Fonseca F.P., Carvalho Mde V., de Almeida O.P., Rangel A.L., Takizawa M.C., Bueno A.G., Vargas P.A. Clinicopathologic analysis of 493 cases of salivary gland tumors in a Southern Brazilian population. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2012;114:230–239. doi: 10.1016/j.oooo.2012.04.008. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Barnes L., Eveson J.W., Reichart P.A., Sidranskiy D. Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours. IARC; Lyon, France: 2005. [(accessed on 26 March 2025)]. World Health Organization Classification of Tumours; pp. 211–281. Available online: https://screening.iarc.fr/doc/BB9.pdf.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

