Impact of Endocrine Therapy on Osteoporosis Risk in Women with Breast Cancer Across Different Hormonal Stages: A Review
- PMID: 40558248
- PMCID: PMC12191915
- DOI: 10.3390/curroncol32060305
Impact of Endocrine Therapy on Osteoporosis Risk in Women with Breast Cancer Across Different Hormonal Stages: A Review
Abstract
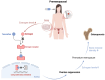
Breast cancer is the leading cause of death among women, and its treatment often involves chemotherapy and hormone therapy, which can compromise bone mineral density (BMD). Tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor modulator, has different effects depending on the patient's hormonal status. On the one hand, in postmenopausal women, it has a protective effect on BMD; on the other hand, in premenopausal women, it can accelerate bone loss, increasing the risk of osteoporosis and fractures. The reduction in estrogen levels during treatment is a key factor in this bone loss. This review underscores the importance of early risk assessment and regular monitoring of bone mineral density, along with the adoption of individualized pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies, such as calcium and vitamin D supplementation and physical exercise, to preserve bone health in premenopausal women with breast cancer undergoing endocrine therapy.
Keywords: breast cancer; osteoporosis; personalized medicine; premenopausal; rehabilitation; tamoxifen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Menon G., Alkabban F.M., Ferguson T. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2024. [(accessed on 6 February 2025)]. Breast Cancer. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29493913/ - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

