Advances in Hydrogel-Integrated SERS Platforms: Innovations, Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects in Food Safety Detection
- PMID: 40558445
- PMCID: PMC12190936
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15060363
Advances in Hydrogel-Integrated SERS Platforms: Innovations, Applications, Challenges, and Future Prospects in Food Safety Detection
Abstract
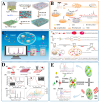
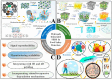
Background: Food safety remains a global concern due to biological and chemical contaminants, including adulterants, pathogens, antibiotic residues, and pesticides. Traditional detection methods are accurate but limited by time requirements, complex sample preparation, high costs, and poor field applicability. Surface-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) offers non-destructive analysis with low detection limits and high specificity, yet conventional SERS substrates face challenges with reproducibility, nanoparticle aggregation, and sensitivity in food matrices. Hydrogels have emerged as supporting materials for SERS due to their water content, tunable porosity, flexibility, and ability to entrap plasmonic nanostructures. Scope and Approach: This review examines recent advances in hydrogel-integrated SERS platforms for food safety applications. The three-dimensional structure of hydrogels enables homogeneous distribution of metal nanoparticles, prevents aggregation, and offers analyte enrichment. We analyze material design, functionalization strategies, and how hydrogel properties-crosslinking density, porosity, surface charge, and nanoparticle distribution-influence SERS performance in food matrices. Key Findings and Conclusions: Hydrogel-integrated SERS platforms demonstrate superior performance in detecting various food contaminants-including pesticides, adulterants, and additives-in real food matrices, often achieving detection limits in the nanomolar to picomolar range, depending on the analyte and substrate design. Current limitations include storage stability concerns, batch-to-batch variability, and regulatory acceptance hurdles. Future research directions should focus on multiplex detection capabilities, integration with smart sensing technologies, and industrial scalability to facilitate practical deployment in global food safety monitoring across diverse supply chains.
Keywords: food safety detection; hydrogel; nanoparticle stabilization; smart materials; surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- WHO WHO global strategy for food safety Report by the Director-General. Nutr. Food Saf. 2021;EB150/25:1–7.
-
- Fakhlaei R., Babadi A.A., Ariffin N.M., Xiaobo Z. Development of FTIR-ATR spectra and PLS regression combination model for discrimination of pure and adulterated acacia honey. Food Control. 2025;169:110996. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2024.110996. - DOI
-
- Gao S., Yang W., Zheng X., Wang T., Zhang D., Zou X. Advances of nanobody-based immunosensors for detecting food contaminants. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2025;156:104871. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2025.104871. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

