Polypyrrole Coatings as Possible Solutions for Sensing and Stimulation in Bioelectronic Medicines
- PMID: 40558448
- PMCID: PMC12190311
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15060366
Polypyrrole Coatings as Possible Solutions for Sensing and Stimulation in Bioelectronic Medicines
Abstract
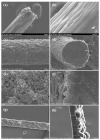
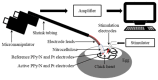
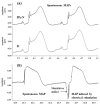
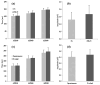
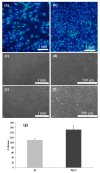
Bioelectronic medicines record biological signals and provide electrical stimulation for the treatment of diseases. Advanced bioelectronic therapies require the development of electrodes that match the softness of the implanted tissues, as the present metal electrodes do not meet this condition. The objective of the present work was to investigate whether the electroconductive polymer polypyrrole (PPy) could be used for fabricating such electrodes, as PPy is several orders softer than metals. For this purpose, we here investigated if electrodes made using coatings and films of PPy doped with naphthalin-2-sulfonic acid (PPy/N) are capable to record and elicit by stimulation cardiac monophasic action potentials (MAPs) and if PPy/N is also biocompatible. The results of this study showed that the tested PPy/N electrodes are capable of recording MAPs almost identical to the MAPs recorded with platinum electrodes and eliciting stimulation-evoked MAPs almost identical to the spontaneous MAPs. In addition, we show here that the cell cultures that we used for biocompatibility tests grew in a similar manner on PPy/N and platinum substrates. We, therefore, conclude that PPy/N coatings and films have recording and electrical stimulation capabilities that are similar to those of platinum electrodes and that PPy/N substrates are as biocompatible as the platinum substrates.
Keywords: action potentials; bioelectronic medicine; polypyrrole; recording; stimulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
References
-
- Mekhail N., Levy R.M., Deer T.R., Kapural L., Li S., Amirdelfan K., Hunter C.W., Rosen S.M., Costandi S.J., Falowski S.M., et al. Long-term safety and efficacy of closed-loop spinal cord stimulation to treat chronic back and leg pain (Evoke): A double-blind, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet Neurol. 2020;19:123–134. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30414-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

