A High-Sensitivity, Bluetooth-Enabled PCB Biosensor for HER2 and CA15-3 Protein Detection in Saliva: A Rapid, Non-Invasive Approach to Breast Cancer Screening
- PMID: 40558468
- PMCID: PMC12190843
- DOI: 10.3390/bios15060386
A High-Sensitivity, Bluetooth-Enabled PCB Biosensor for HER2 and CA15-3 Protein Detection in Saliva: A Rapid, Non-Invasive Approach to Breast Cancer Screening
Abstract
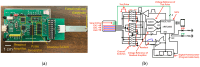
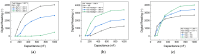
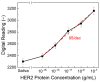
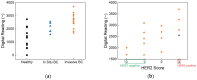
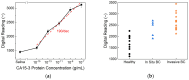
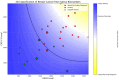
Breast cancer is a leading cause of cancer-related mortality worldwide, requiring efficient diagnostic tools for early detection and monitoring. Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) is a key biomarker for breast cancer classification, typically assessed using immunohistochemistry (IHC). However, IHC requires invasive biopsies and time-intensive laboratory procedures. In this study, we present a biosensor integrated with a reusable printed circuit board (PCB) and functionalized glucose test strips designed for rapid and non-invasive HER2 detection in saliva. The biosensor achieved a limit of detection of 10-15 g/mL, 4 to 5 orders of magnitude more sensitive than the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), with a sensitivity of 95/dec and a response time of 1 s. In addition to HER2, the biosensor also detects cancer antigen 15-3 (CA15-3), another clinically relevant breast cancer biomarker. The CA15-3 test demonstrated an equally low limit of detection, 10-15 g/mL, and a higher sensitivity, 190/dec, further validated using human saliva samples. Clinical validation using 29 saliva samples confirmed our biosensor's ability to distinguish between healthy, in situ breast cancer, and invasive breast cancer patients. The system, which integrates a Bluetooth Low-Energy (BLE) module, enables remote monitoring, reduces hospital visits, and enhances accessibility for point-of-care and mobile screening applications. This ultra-sensitive, rapid, and portable biosensor can serve as a promising alternative for breast cancer detection and monitoring, particularly in rural and underserved communities.
Keywords: CA15-3; HER2; biomarker; biosensor; breast cancer; high sensitivity; non-invasive; printed circuit board; saliva; screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Enzyme-free and highly sensitive detection of human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 based on MNAzyme signal amplification in breast cancer.J Mater Chem B. 2024 Dec 18;13(1):305-311. doi: 10.1039/d4tb01813c. J Mater Chem B. 2024. PMID: 39539244
-
Using Ru-PdO@MXenes-Nanostructured Electrochemical Immunosensing System for Selective Detection of Multiple Breast Biomarkers (HER2 and MUC1).ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025 Jul 21;8(7):5743-5756. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.5c00452. Epub 2025 Jun 9. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2025. PMID: 40489703
-
A Comparison Between Immunohistochemistry and mRNA Expression to Identify Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Low Breast Cancer.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2025 Jul 1;149(7):635-642. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2024-0255-OA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2025. PMID: 39471829
-
Mammography in combination with breast ultrasonography versus mammography for breast cancer screening in women at average risk.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Mar 31;3(3):CD009632. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009632.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36999589 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
References
-
- Society A.C. Key Statistics for Breast Cancer. [(accessed on 5 May 2025)]. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/breast-cancer/about/how-common-is-br....
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

