5' DREDGE: Direct Repeat-Enabled Downregulation of Gene Expression via the 5' UTR of Target Genes
- PMID: 40558493
- PMCID: PMC12191184
- DOI: 10.3390/cells14120866
5' DREDGE: Direct Repeat-Enabled Downregulation of Gene Expression via the 5' UTR of Target Genes
Abstract
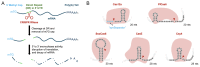
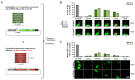
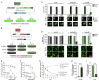
Despite the availability of numerous methods for controlling gene expression, there remains a strong need for technologies that maximize two key properties: selectivity and reversibility. To this end, we developed a novel approach that exploits the highly sequence-specific nature of CRISPR-associated endoribonucleases (Cas RNases), which recognize and cleave short RNA sequences known as direct repeats (DRs). In this approach, referred to as DREDGE (direct repeat-enabled downregulation of gene expression), selective control of gene expression is enabled by introducing one or more DRs into the untranslated regions (UTRs) of target mRNAs, which can then be cleaved upon expression of the cognate Cas RNase. We previously demonstrated that the expression of target genes with DRs in their 3' UTRs are efficiently controlled by the DNase-dead version of Cas12a (dCas12a) with a high degree of selectivity and complete reversibility. Here, we assess the feasibility of using DREDGE to regulate the expression of genes with DRs inserted in their 5' UTRs. Among the five different Cas RNases tested, Csy4 was found to be the most efficient in this context, yielding robust downregulation with rapid onset in doxycycline-regulatable systems targeting either a stably expressed fluorescent protein or an endogenous gene, both in a fully reversible manner. Unexpectedly, dCas12a was also found to be modestly effective despite binding essentially irreversibly to the cut mRNA on its 5' end and thereby boosting mRNA levels. Our results expand the utility of DREDGE as an attractive method for regulating gene expression in a targeted, highly selective, and fully reversible manner.
Keywords: CRISPR; DREDGE; direct repeat; endoribonuclease; gene regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signs and symptoms to determine if a patient presenting in primary care or hospital outpatient settings has COVID-19.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013665. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013665.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593186 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Control of Gene Expression Using CRISPR-Associated Endoribonucleases.Cells. 2025 Apr 3;14(7):543. doi: 10.3390/cells14070543. Cells. 2025. PMID: 40214496 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic test accuracy and cost-effectiveness of tests for codeletion of chromosomal arms 1p and 19q in people with glioma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Mar 2;3(3):CD013387. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013387.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35233774 Free PMC article.
-
Antidepressants for pain management in adults with chronic pain: a network meta-analysis.Health Technol Assess. 2024 Oct;28(62):1-155. doi: 10.3310/MKRT2948. Health Technol Assess. 2024. PMID: 39367772 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic pharmacological treatments for chronic plaque psoriasis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Apr 19;4(4):CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub4. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 23;5:CD011535. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD011535.pub5. PMID: 33871055 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

