The Role of Targeted Microbiota Therapy in the Prevention and Management of Puerperal Mastitis
- PMID: 40558587
- PMCID: PMC12191795
- DOI: 10.3390/diseases13060176
The Role of Targeted Microbiota Therapy in the Prevention and Management of Puerperal Mastitis
Abstract
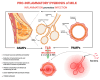
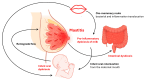
Mastitis, an inflammatory condition of the breast, significantly affects breastfeeding women and can lead to the early cessation of lactation. This article explores the pathophysiology of mastitis, distinguishing between acute mastitis (AM) and subacute mastitis (SAM), with a focus on the microbial dynamics involved. AM is primarily associated with Staphylococcus aureus, while SAM is linked to a dysbiotic milk microbiota characterized by an imbalance of microbial species, including increased levels of opportunistic pathogens. The role of inflammation and the gut-breast axis in the development of mastitis are discussed, emphasizing the importance of maintaining a healthy microbiota. Recent studies highlight the potential of probiotics as a preventive and therapeutic measure against mastitis, showing promising results in reducing incidence and recurrence. However, further research is necessary to optimize probiotic strains, dosages, and treatment protocols. This review underscores the need for a comprehensive understanding of the microbiological, immunological, and inflammatory factors involved in mastitis to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Keywords: breastfeeding; dysbiosis; inflammation; mastitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources