Effect of Potassium-Ion-Triggered Double Helix Aggregation on Shakedown Behavior of κ-Carrageenan/Polyacrylamide Hydrogel
- PMID: 40558710
- PMCID: PMC12191931
- DOI: 10.3390/gels11060412
Effect of Potassium-Ion-Triggered Double Helix Aggregation on Shakedown Behavior of κ-Carrageenan/Polyacrylamide Hydrogel
Abstract
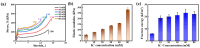
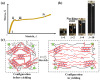
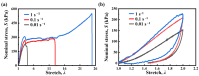
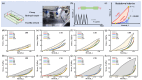
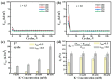
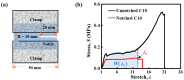
This study investigates the effect of potassium ion (K+) concentration on double helix aggregation in κ-carrageenan-based hydrogels, which significantly influences their shakedown behavior. The shakedown behavior of κ-carrageenan/polyacrylamide (PAAm) hydrogels was characterized by the evolution of maximum stress and energy dissipation during cyclic load. The experimental results indicate that higher K+ concentrations significantly improve the maximum stress in the steady state, but barely influence the energy dissipation in the steady state. The improved maximum stress can be explained by the higher density of double helix aggregation. The steady energy dissipation elucidates that the K+ concentration does not affect the breaking-recovering balance of the sacrificial network in cyclic loading. These results provide mechanistic insights into how ion-triggered double helix aggregation influences the shakedown behavior of κ-carrageenan-based hydrogels.
Keywords: double helices; fatigue damage; shakedown behavior; κ-carrageenan hydrogel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chen X., Liu F., Yu Q., Yang M., Suo Z., Tang J. A Soft and Fatigue-Resistant Material that Mimics Heart Valves. Matter. 2025;8:101926. doi: 10.1016/j.matt.2024.11.020. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

