One-Pot Synthesis of Gelatin/Gum Arabic Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials
- PMID: 40558728
- PMCID: PMC12191848
- DOI: 10.3390/gels11060429
One-Pot Synthesis of Gelatin/Gum Arabic Hydrogels Embedding Silver Nanoparticles as Antibacterial Materials
Abstract
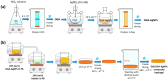
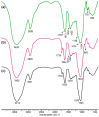
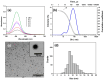
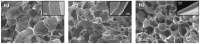
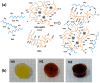
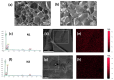
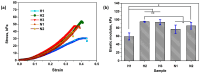
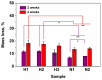
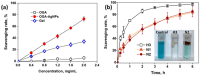
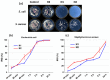
High and large-spectrum antibacterial features and ROS scavenging properties are the most important requirements for efficient wound-dressing materials. A composite hydrogel was synthesized herein by a one-pot procedure embedding silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) covered with oxidized gum arabic (OGA) within gelatin (Gel) hydrogel. Small (2-20 nm), round-shaped AgNPs (ζ = -22 mV) were first obtained by green synthesis using OGA as a reducing and capping agent. Composite hydrogels, containing 0.6 and 1.3 wt.% Ag, were obtained by the covalent cross-linking (Schiff base reaction) of amine groups in gelatin with the dialdehyde groups located on the shell of the AgNPs. Thus, the uniform distribution of the AgNPs in the network contributed to the increased physicochemical and hydrolytic stability of the hydrogels. Moreover, the high swelling degree together with the good mechanical properties make them appropriate candidates for wound-healing materials. The hydrogels exhibited 80% scavenging activity of ABTS●+ free radicals after 6 h of incubation and were effective against E. coli and S. aureus, achieving a 4% survival of bacteria within 3 h (E. coli) and 24 h (S. aureus). These results clearly indicate that the proposed hydrogels have potential in wound-dressing applications.
Keywords: Schiff base reaction; antibacterial; antioxidant; gelatin; oxidized gum arabic; silver nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adhesive and antibacterial dialdehyde microfibrillated cellulose/gelatin hydrogel incorporating core-shell structured AgNPs@PA for wound management.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 Aug;319(Pt 3):145505. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.145505. Epub 2025 Jun 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40571001
-
Schiff Base-Based Hydrogel Embedded with In Situ Generated Silver Nanoparticles Capped by a Hyaluronic Acid-Diethylenetriamine Derivative for Wound Healing Application.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024 Apr 24;16(16):20186-20201. doi: 10.1021/acsami.4c00657. Epub 2024 Apr 11. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2024. PMID: 38603548
-
The Characterization and Study of Antibacterial, Free Radical Scavenging, and Anticancer Potential of Livistona chinensis-Mediated Silver Nanoparticles.Molecules. 2023 Nov 25;28(23):7773. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237773. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067504 Free PMC article.
-
Hydrogel dressings for venous leg ulcers.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Aug 5;8(8):CD010738. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD010738.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35930364 Free PMC article.
-
Dressings and topical agents for the management of open wounds after surgical treatment for sacrococcygeal pilonidal sinus.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 May 20;5(5):CD013439. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013439.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022. PMID: 35593897 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mushtaq F., Raza Z.A., Batool S.R., Zahid M., Onder O.C., Rafique A., Nazeer M.A. Preparation, properties, and applications of gelatin-based hydrogels (GHs) in the environmental, technological, and biomedical sectors. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022;218:601–633. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.07.168. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Mohanto S., Narayana S., Merai K.P., Kumar J.A., Bhunia A., Hani U., Al Fatease A., Gowda B.H.J., Nag S., Ahmed M.G., et al. Advancements in gelatin-based hydrogel systems for biomedical applications: A state-of-the-art review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023;253:127143. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127143. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

